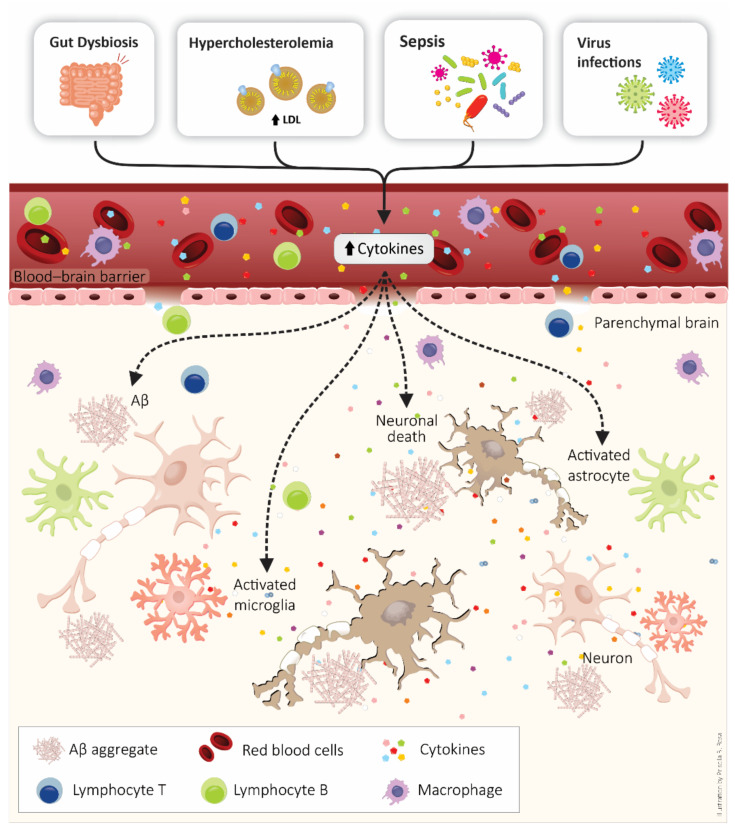
Figure 2.
Peripheral diseases are a risk factor for β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) peptide accumulation, neurodegeneration, and Alzheimer’s disease development. Systemic inflammatory conditions, such as metabolic disease, sepsis, virus infections, and dysbiosis, are associated with blood–brain barrier (BBB) disruption and coexistent neuroinflammation. Neuroinflammation is characterized by the presence of the peripheral immune system, activation of glial cells (astrocytes and microglia), and increased production of pro-inflammatory molecules (e.g., cytokines).