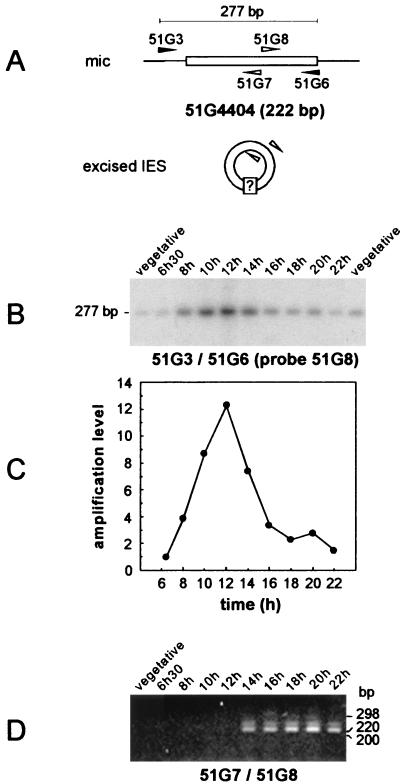
FIG. 2.
Timing of IES 51G4404 excision and detection of joined IES ends in synchronized exconjugant cells. (A) Diagram of the PCR strategies used for the amplification of chromosomal IES 51G4404 prior to its excision (primers 51G3 and 51G6 [black arrowheads]) and for the detection of putative IES circular forms (primers 51G7 and 51G8 [white arrowheads]). (B) Southern blot analysis of the PCR products amplified from synchronized exconjugant cells with primers 51G3 and 51G6. Samples were revealed with 32P-labeled oligonucleotide 51G8 after electrophoresis on a 3% NuSieve gel. Indicated time points refer to the time following the mixing of reactive cells. Two independent samples of 10 vegetative cells were used as controls for the micronuclear signal. (C) Quantitative analysis of the timing of IES 51G4404 excision. The signals shown in panel B were quantified and normalized relative to the value obtained for the 6 h 30 min time point. (D) PCR amplification from the same NP-40-treated synchronized exconjugant cells as in panel B, using divergent primers 51G7 and 51G8 (see Materials and Methods). PCR products were run on a 3% NuSieve gel and revealed by ethidium bromide staining. The lane order is as in panel B, except that only one vegetative control was used.