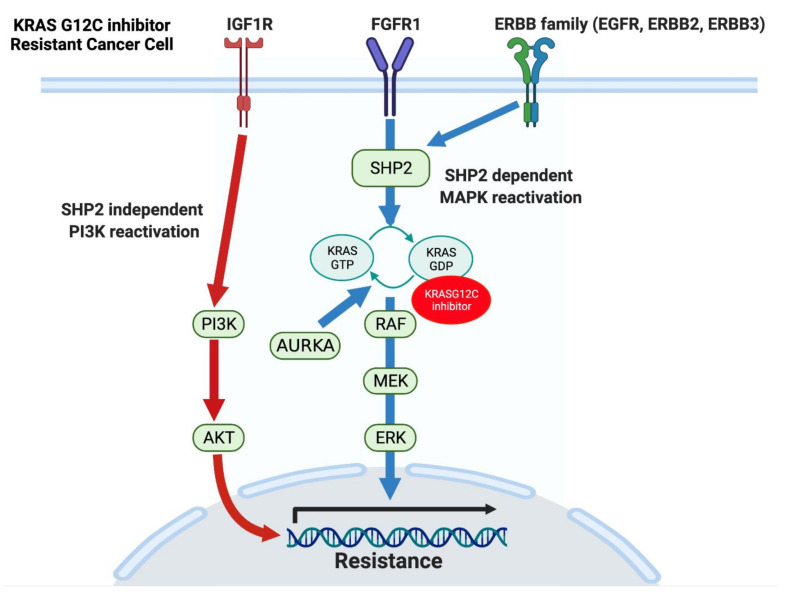
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of resistance to KRAS G12C inhibitors. Inhibition of MAPK signaling by G12C inhibitors induces feedback reactivation of MAPK via multiple receptor tyrosine kinases, including FGFR1 and ERBB family members. While FGFR1 and ERBB3 reactivate the MAPK signaling pathway through adaptor protein SHP2, IGF1R leads to SHP2-independent activation of the PI3K signaling pathway. Additionally, activation of EGFR and Aurora kinase following KRAS G12C inhibitor treatment leads to protein synthesis and activation of KRAS G12C. The newly synthesized and activated G12C proteins are resistant to KRAS G12C inhibition due to their GTP-bound form. Furthermore, mutations in MAPK proteins can induce constitutive MAPK activation in the presence of KRAS G12C inhibitors. Activation of PI3K and MAPK leads to transcription of genes related to cell proliferation and survival (black arrow). Abbreviations: EGFR, Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERBB, Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase; FGFR1, Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; IGF1R, Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; SHP2, Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2.