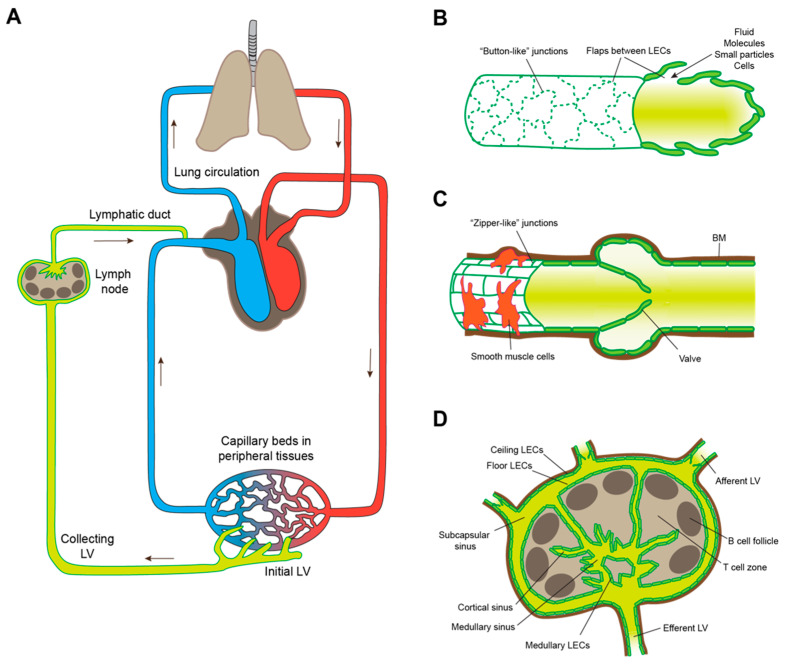
Figure 1.
Overview of the lymphatic system. (A) Integrated schematic representation of the blood circulation and the lymphatic system. LV: lymphatic vessel. (B) Anatomical characteristics of initial lymphatic vessels. The individual LECs are irregularly shaped and partly overlapping. Junctions between LECs are discontinuous (“button-like”), facilitating intravasation of fluid, molecules, particles, and entire cells from the interstitium via LEC flaps. (C) Anatomical characteristics of collecting lymphatic vessels. The LECs are regularly shaped and form tight junctions (“zipper-like”) between them. Perivascular smooth muscle cells support the vessel and allow it to contract. Furthermore, collecting lymphatic vessels have a continuous basement membrane (BM) and valves to ensure unidirectional lymph transport. (D) Schematic representation of a lymph node with afferent and efferent lymphatic vessels, various types of sinuses, and corresponding LEC subsets.