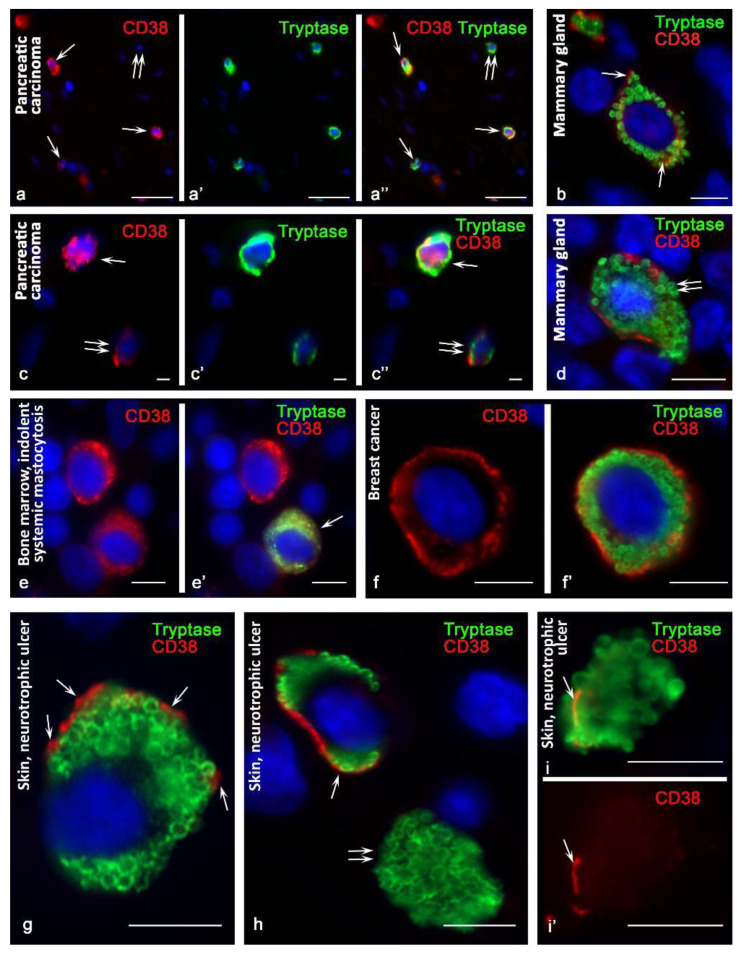
Figure 1.
CD38 cytotopography in mast cells. Primary antibodies used: (a–e) rabbit monoclonal (Cell Marque, USA); (f–i) mouse monoclonal (kindly provided by Fabio Malavasi, University of Torino, Italy). (a–a″) Pancreatic carcinoma. Cells with expression (arrowed) and without expression (double arrow) of CD38 are identified. (b) The mammary gland. Expression of CD38 in the cytoplasm and on the plasma membrane (indicated by an arrow). (c–c″) Pancreatic carcinoma. MCs with high (arrow) and moderate (double arrow) CD38 expression. (d) The mammary gland. The predominantly peripheral location of CD38 in the area of the plasma membrane, with varying severity along its length. At the site of secretion of tryptase, CD38 is absent (double arrow). (e,e′) Indolent systemic mastocytosis, bone marrow. Diffuse distribution of CD38 in the cytoplasm of a hypogranulated mast cell (indicated by an arrow). (f,f′) Breast cancer. Preferential peripheral location of CD38. (g) Skin. Peripheral localization of CD38 at some loci of the plasma membrane (indicated by an arrow). (h,i,i′) Skin, neurotrophic ulcer. (h) MCs with CD38 expression on plasmalemma (arrowed) and absent (double arrow). (i,i′) Expression of the exoenzyme at the peripheral locus of the non-nuclear cytoplasmic fragment of the mast cell (indicated by the arrow). Scale bar: 50 µm (a–a″), 5 µm (all others).