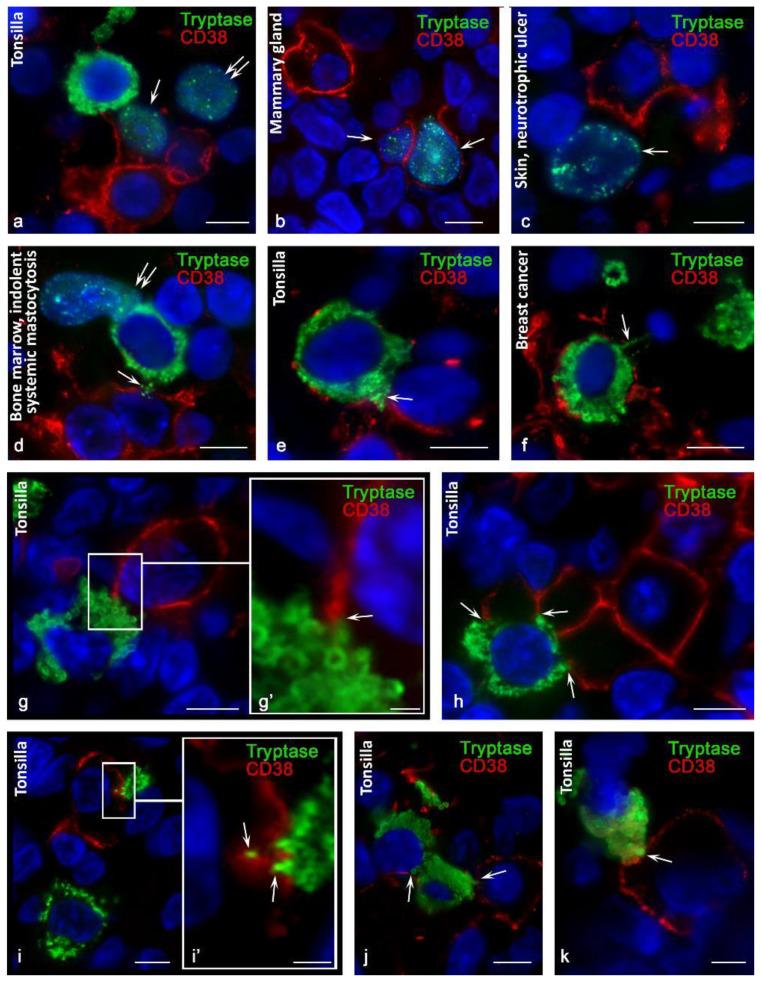
Figure 3.
Features of the interaction of mast cells with CD38+ cells in a specific tissue microenvironment. Primary antibodies used: (a,b,h–k) rabbit monoclonal (Cell Marque, USA); (c–g) mouse monoclonal (kindly provided by Fabio Malavasi, University of Torino, Italy). (a) Tonsilla. Mast cell in contact with CD38+ cells; localization of tryptase in the nucleus of CD38-positive and CD38-negative cells (arrow and double arrow, respectively). (b) The mammary gland. The location of mast cell tryptase in the nuclei of CD38+ cells (indicated by an arrow). (c) Skin, neurotrophic ulcer. Tryptase in the nucleus of CD38-negative cell. (d) Indolent systemic mastocytosis, bone marrow. Directed secretion of mast cell tryptase into a CD38-positive cell (arrow); tryptase in the nucleus of an adjacent CD38-negative cell (double arrow). (e) Tonsilla. The CD38+ mast cell makes contact over a large area with the CD38+ cell (indicated by the arrow). (f) Breast cancer. Mast cell in close contact with CD38+ cells; secretion of tryptase towards the nucleus of the adjacent cell (arrow). (g–k) Tonsilla. Various variants of tryptase secretion and contact of mast cell granules with the plasmalemma of CD38+ cells (indicated by an arrow). Scale bar: 1 µm (g′,i′), 5 µm (all others).