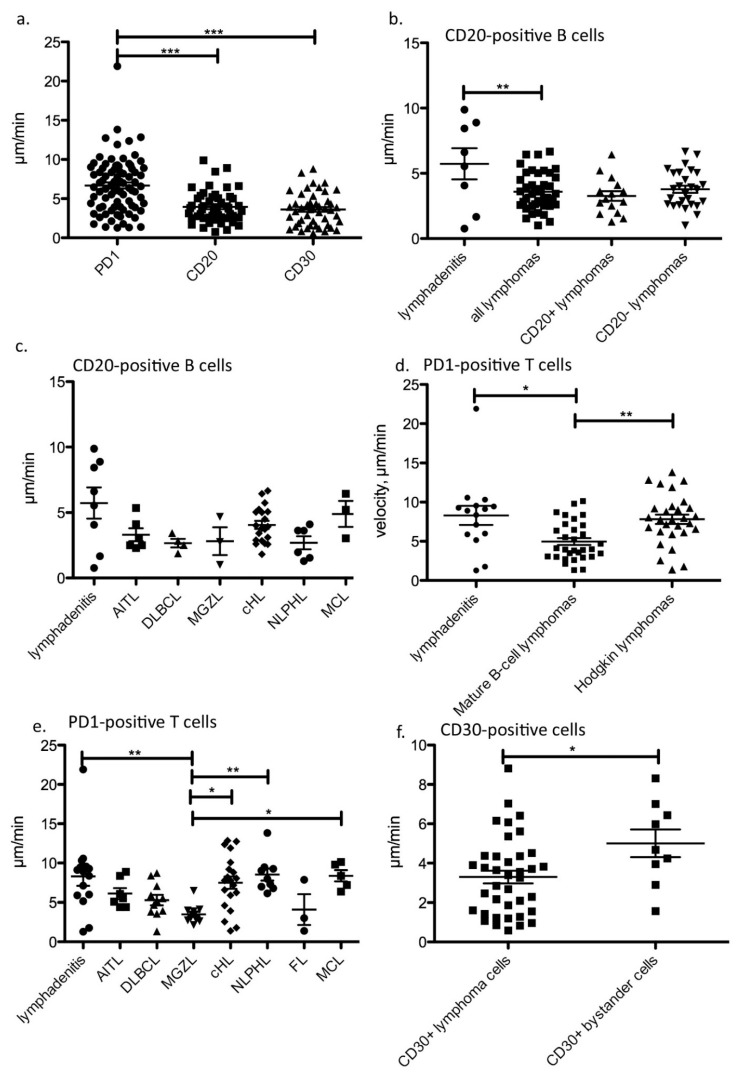
Figure 1.
Velocity of different cell types under reactive and neoplastic conditions. (a). Velocity of PD1-positive T cells, CD20-positive B cells and CD30-positive cells in all cases studied (*** p < 0.001, one-way-ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-test for multiple comparisons). Each dot represents the mean from one movie. (b). Velocity of CD20-positive B cells in lymphadenitis and malignant lymphomas. The velocity of bulk CD20-positive B cells in CD20+ lymphomas largely represents the velocity of tumor cells, whereas the velocity in CD20- lymphomas corresponds to reactive bystander B cells. (** p = 0.0042, unpaired t-test.) Each dot represents the mean from one movie. (c). Velocity of CD20-positive B cells listed according to different lymphoma entities. No significant differences were observed. Each dot represents the mean from one movie. Lymphadenitis: 4 cases, AITL, DLBCL and MCL: one case, MGZL and NLPHL: two cases, cHL: three cases. (d). Velocity of PD1-positive T cells grouped according to diagnosis of lymphadenitis, mature B-cell lymphomas and Hodgkin lymphomas. Each dot represents the mean from one movie. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test for multiple comparisons. (e). Velocity of PD1-positive T cells according to lymphoma entities. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, Kruskal–Wallis-Test with Dunn´s post-test for multiple comparisons. Each dot represents the mean from one movie. Lymphadenitis: 5 cases, AITL and MCL: one case, MGZL, DLBCL, FL and NLPHL: two cases, cHL: three cases. (f). Velocity of CD30-positive lymphoma cells compared with CD30-positive reactive bystander cells in CD30-negative lymphomas and lymphadenitis (* p < 0.05, unpaired t-test). Each dot represents the mean from one movie.