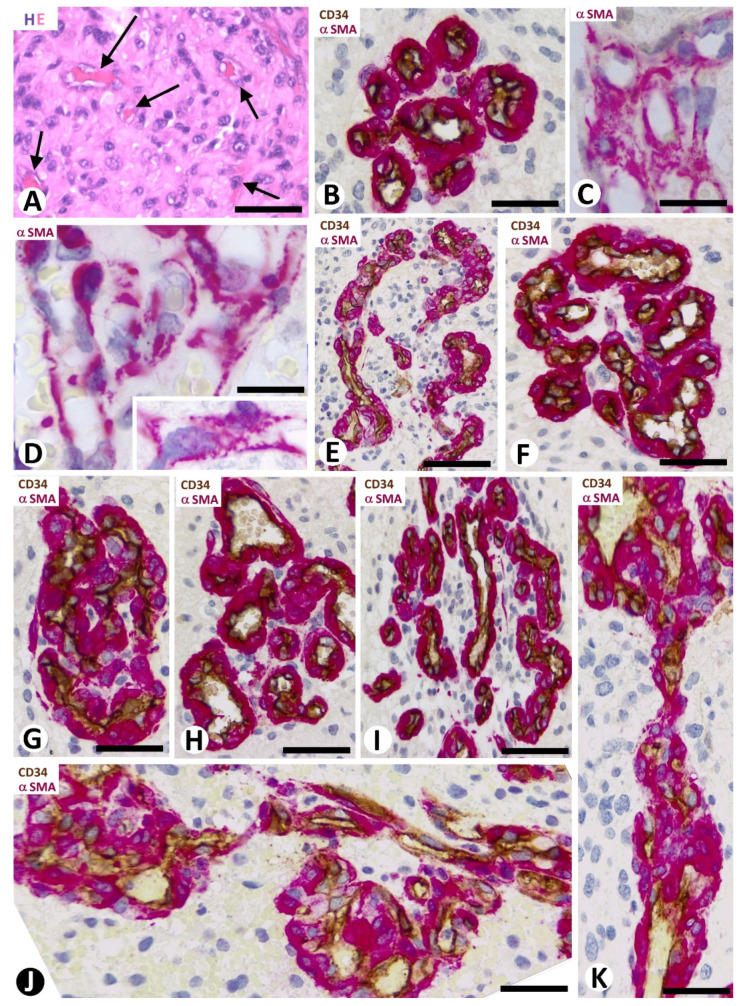
Figure 1.
Vascular patterns and transitional structures in GBM. (A) “Classic” pattern with delicate capillaries (arrows). (B–G) Patterns of vascular clusters (B–D), vascular garlands (E), and glomeruloid bodies (F,G), which form the bizarre microvasculature (BM). In vascular clusters, note the different characteristics of pericytes (red) in Type I (B) or Type II (C,D) BM. (H,I) Transitional structures between vascular garlands and glomeruloid bodies. (J,K) Glomeruloid bodies are observed originating from vessels of varying size and transitional structures. (A) Hematoxylin staining. (B,E–K) Double immunochemistry for CD34 (brown, vascular endothelium) and αSMA (red, pericytes). Hematoxylin counterstain. (C,D) Immunochemistry for αSMA. Hematoxylin counterstain. Bars: (A) 150 µm, (B–D,F,J,K) 40 µm, and (E,G–I) 45 µm.