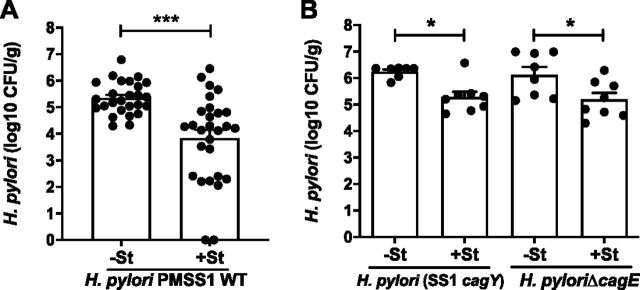
FIG 2.
Salmonella coinfection decreases H. pylori colonization. (A) Colonization of WT H. pylori in the stomach was decreased 8 weeks p.i. in Salmonella-coinfected animals (+St) compared to that in animals with H. pylori infection alone (−St). (B) Colonization with H. pylori SS1cagY (PMSS1 with cagY from SS1) and H. pylori ΔcagE, which have defective T4SSs, was also decreased when mice were coinfected with Salmonella. Each data point represents one mouse. Bars indicate means ± SEMs. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.005.