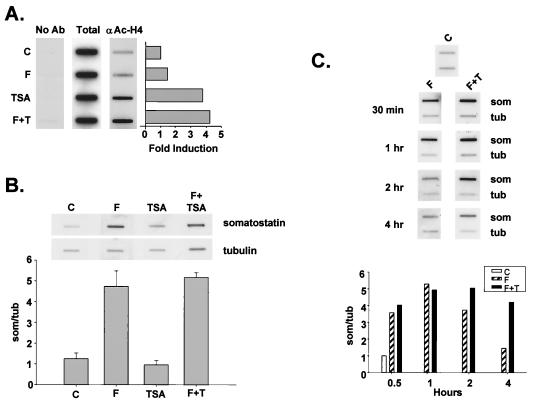
FIG. 2.
HDAC inhibitors stimulate CREB activity during the late attenuation phase of transcription in response to cAMP. (A) ChIPs of untreated D5 cells (C) or D5 cells treated with forskolin (F) or TSA (T), either separately or in combination. Following a 30-minute stimulation, cells were treated with formaldehyde, and the cross-linked histone-DNA complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-acetylated H4-specific antiserum. DNA recovered from each immunoprecipitation was analyzed for somatostatin gene sequences by slot blot hybridization with 32P-labeled somatostatin cDNA. No Ab, no primary antibody during immunoprecipitation; Total, 10% of total somatostatin hybridizing sequences applied to the immunoprecipitation reaction; αAc-H4, somatostatin hybridizing sequences that coimmunoprecipitate with somatostatin promoter sequences compared to control cells as shown in the bar graph. (B) Nuclear run-on transcription assay of D5 cells treated without (C) or with forskolin (F), TSA, or forskolin plus TSA for 30 min. 32P-labeled transcripts were hybridized to slot-blotted cDNAs encoding either somatostatin (som) or α-tubulin (tub). The bar graph shows mean ± standard error (n = 3) for each treatment. (C) Representative run-on transcription assay (n = 2) showing time course of somatostatin transcription in response to forskolin and HDAC inhibitor. D5 cells were treated with control vehicle (C), forskolin (F), or forskolin plus TSA (F+T) for times shown, and cells were harvested for run-on assay as described above. The bar graph shows relative somatostatin transcription rate in control and treated D5 cells normalized to tubulin.