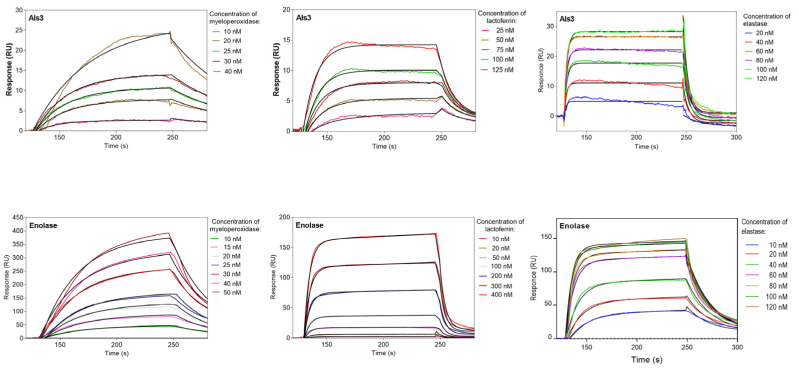
Figure 5.
Binding of selected NET-composing proteins to immobilized fungal cell surface proteins―Als3 and enolase. The kinetic analysis of the binding properties of selected fungal proteins was performed using a BIACORE 3000 system with the detection of surface plasmon resonance changes (RU) during the NET-protein binding to the immobilized Als3 and enolase on the surface of CM5 chips. For the protein immobilization, the standard amine-coupling procedure was used. The immobilization level was 800 RU and 400 RU for Als3 and enolase, respectively. The selected host protein solutions were injected over the chip surface with a flow rate of 30 µL/min, for 2 min for association and 2 min for dissociation processes. For the chip surface regeneration, a pulse of 1 M NaCl (30 s) or 0.1% of SDS (10 s) was used, according to the manufacturer-recommended procedure. The data from three independent tests were analyzed by BIAevaluation software version 4.1 (GE Healthcare). For each dataset, the simultaneous fitting of constants for association and dissociation rates was used with the 1:1 Langmuir binding model.