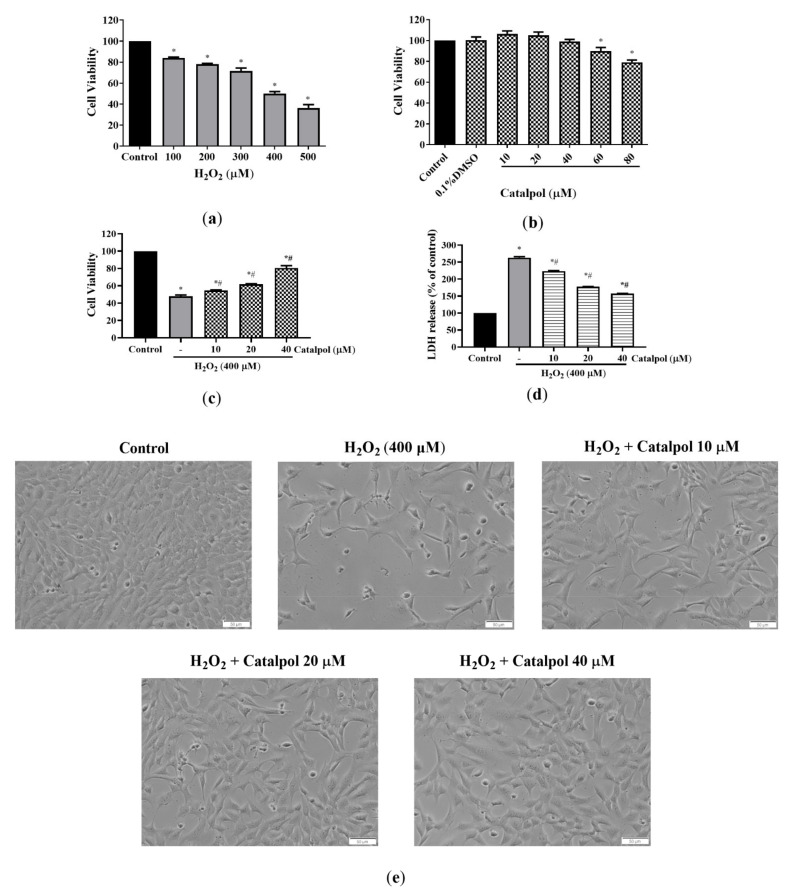
Figure 1.
Catalpol protected RPE cells from H2O2-induced cell damage. (a) ARPE-19 cells were first exposed to different concentrations of H2O2 (100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 μM) for 6 h, and cell viability was determined with MTT assay. (b) Effect of different concentrations of catalpol on ARPE-19 cell viability. (c) Cytoprotective effect of catalpol. ARPE-19 cells were pretreated with varying concentrations of catalpol (10, 20, and 40 μM) for 24 h, and then H2O2 (400 μM) was added and the treatment was continued for 6 h. Cell viability was measured with MTT assay. (d) ARPE-19 cells were pretreated with catalpol (10–40 μM) for 24 h before being exposed to H2O2 (400 μM) for 6 h. The release of LDH was measured using an LDH cytotoxicity assay kit. (e) Changes in the number of ARPE-19 cells were observed and presented (original magnification: 200×). Data are presented as mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments (* p < 0.05 vs. control group, # p < 0.05 vs. H2O2 (400 μM)-treated group).