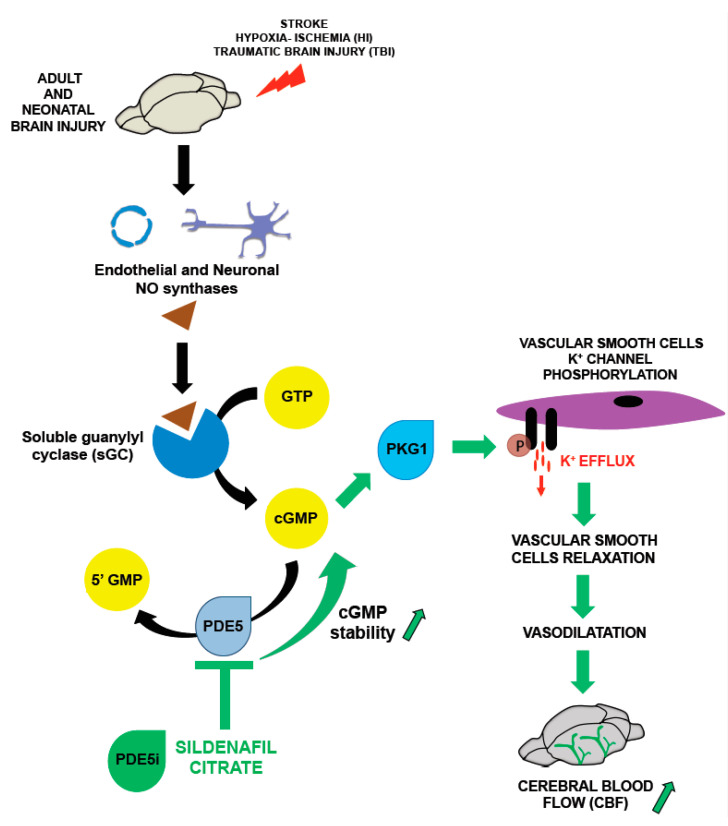
Figure 1.
Sildenafil and the modulation of cerebral blood flow (CBF): the binding of NO to sGC, the main NO physiological receptor, stimulated the synthesis of cGMP, which binds to and activates cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (PKG1). Activated PKG1 then phosphorylates the alpha subunit of the vascular smooth cell K+ channel, resulting in a K+ efflux, cell hyperpolarization, vascular smooth cell relaxation and in an increase of CBF. Sildenafil modulate cGMP stability via inhibition of the enzyme PDE5 that catalyzes the conversion of cGMP into the 5′ GMP inactive form.