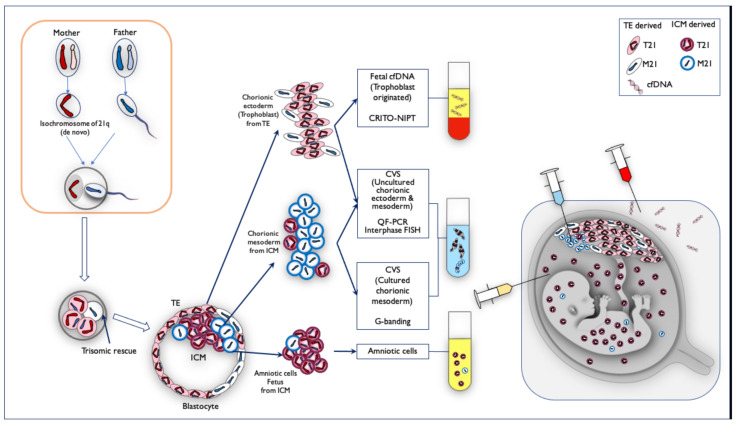
Figure 11.
The mechanism of mosaicism in Case Mo4, in which the frequency of monosomy/disomy/trisomy mosaicism differed among specimens. First, the oocytes of de novo isochromosome 21 were formed during the meiosis of the mother, and the fertilized eggs became T21 with the mother-derived isochromosome 21. The M21 cell line arose because of trisomic rescue at the early stage before the blastocyst. Both trophectoderm (TE) and the internal cell mass (ICM) in the blastocyst became mosaicism of Robertsonian T21 and M21. On the basis of the genetic results, we estimated the mosaic ratio. TE-derived chorionic ectoderm (trophoblast) was probably Robertsonian T21-dominant, and fetal cfDNA is derived from trophoblast, so CRITO-NIPT was T21-positive. The DNA from uncultured cells in the CVS samples was a mixture of both uncultured chorionic ectoderm from TE (T21 predominant), and chorionic mesoderm from ICM (M21 predominant). The cultured chorionic mesoderm was a mosaicism of predominantly M21-cells in ICM. Therefore, the CVS G-banding result was M21, which was completely different from the CRITO-NIPT result of T21. On the other hand, amniotic fluid cells and fetal cells were derived from T21-dominant ICM sites, which may have led to the Robertsonian T21 results.