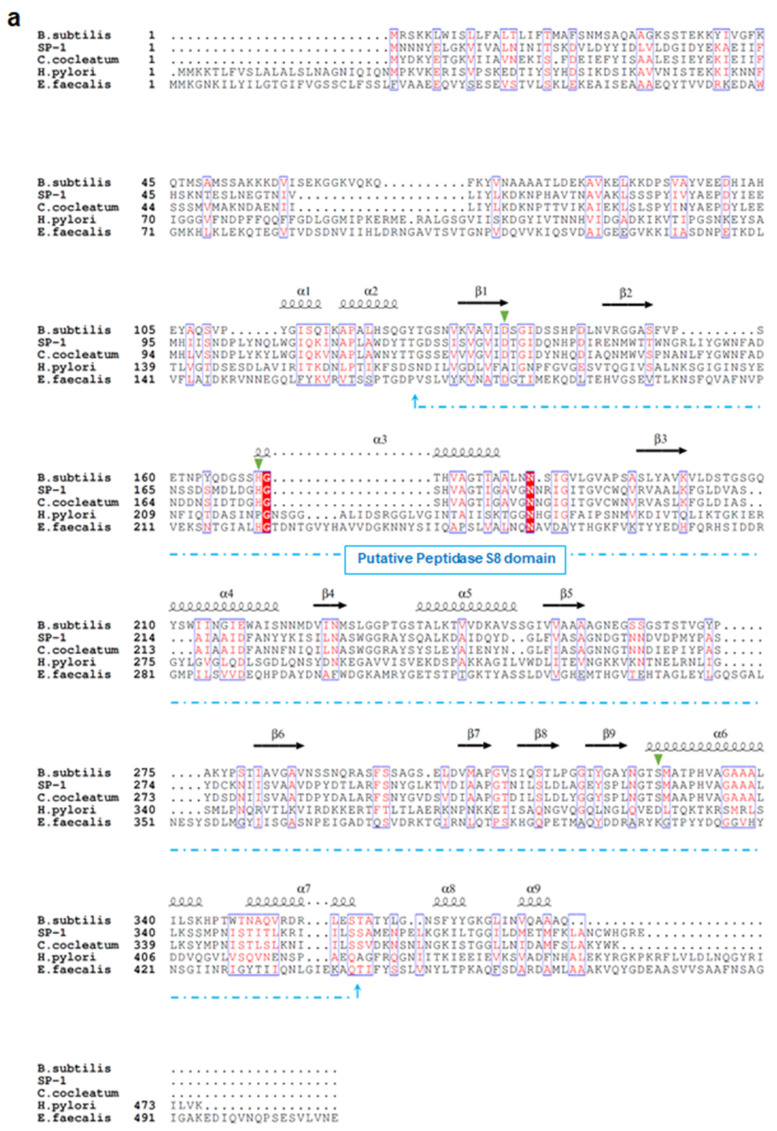
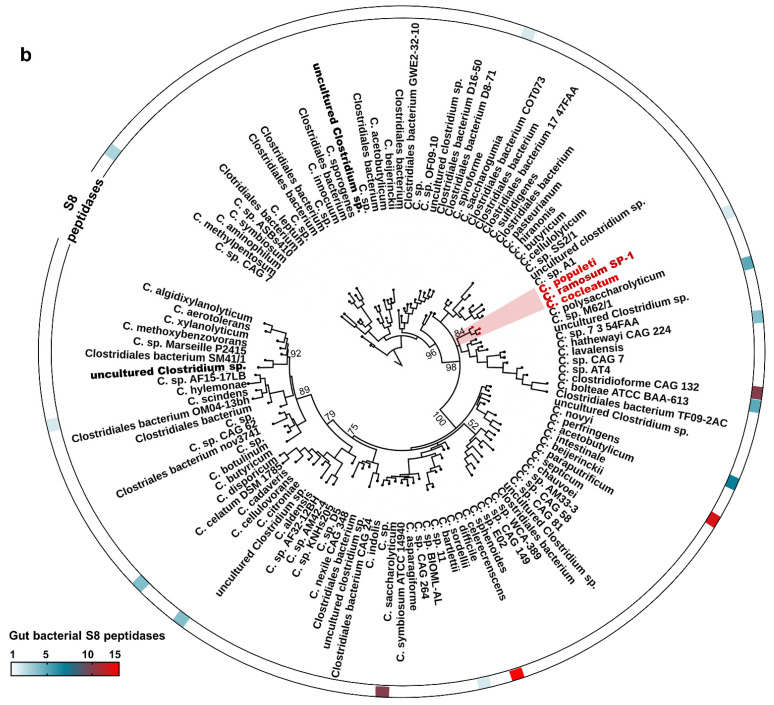
Figure 1.
Sequence analysis and phylogeny of Clostridium-producing proteases. (a) Structure-based sequence alignment of SP-1 and other selected bacterial proteases (UniProt accession numbers: E1S7U4, protease from H. pylori; Q833V7, gelatinase from E. faecalis; A0A1I0FUC9, protease from C. cocleatum and P04189, Subtilisin from B. subtilis). The structural elements shown above the alignment were generated using the Subtilisin structure (PDB ID: 6O44). Invariant residues between sequences are typed red on a white background, and conserved residues are shown as white letters on a red background. Green triangles represent conserved amino acids from the catalytic triad, Asp134, His175, and Ser327. (b) Distribution of subtilisin-like proteases across gut Clostridium species. Clostridium sequences with >40% identity to SP-1 are clustered into a subclade highlighted in red. Branch labels show bootstrap values. Outer tracks show the numbers of genes from each S8 subtilisin-like protease in each genome.