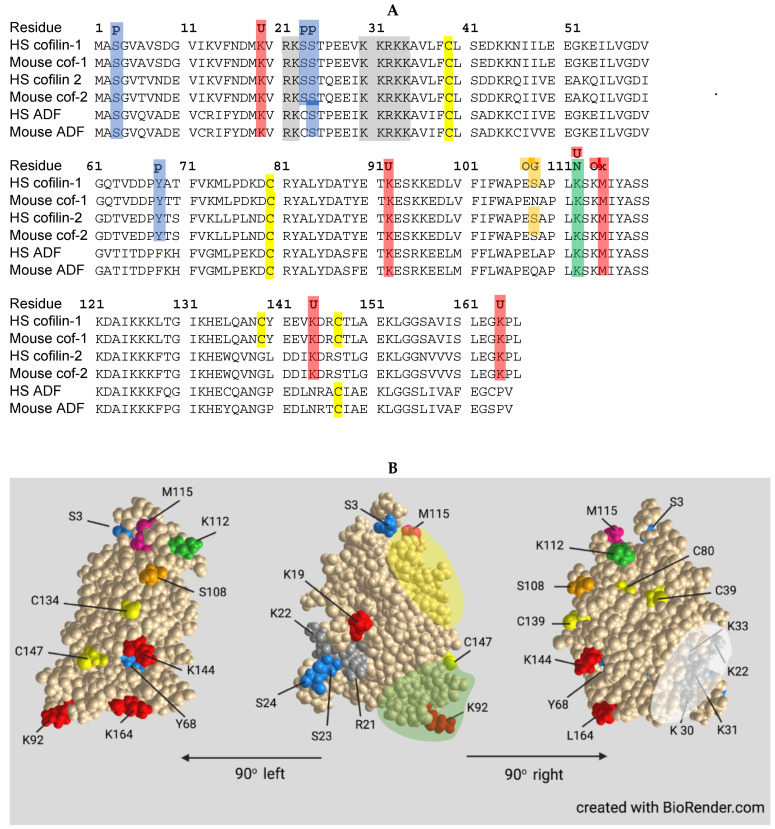
Figure 4.
Primary sequence comparison and 3D structure of ADF/cofilins. (A): Aligned sequences of human (HS) and mouse cofilin 1, cofilin 2, and ADF, identifying sites for regulation and modification discussed in the text: (p-blue) phosphorylation; (U-red) ubiquitinylation; (gray highlight) bipartite nuclear localization sequence; (OG- orange) O-GlcNAcylation; (N-green) neddylation (also a ubiquitinylation site); and (Ox) Methionine oxidation. Cysteines are highlighted in yellow: C39-C147 forms an intermolecular disulfide found in rods, and C39-C80 and C139-C147 form intramolecular disulfides in response to oxidative stress that targets cofilin to mitochondria [63,64,65]. Residues that could account for differences in regulation between isoforms or between human and mouse are 68, 108, 139, 144 and 164. (B): Structure of human cofilin-1 viewed facing the actin-binding side with 90° rotations for side views. Residue colors match as close as possible with those used in A. Green highlight in center image is the lower F-actin interface, and yellow highlight is the upper F-actin–G-actin interface. Sequence data and 3D protein structure from NCBI using Cn3D software version 4.3.1.