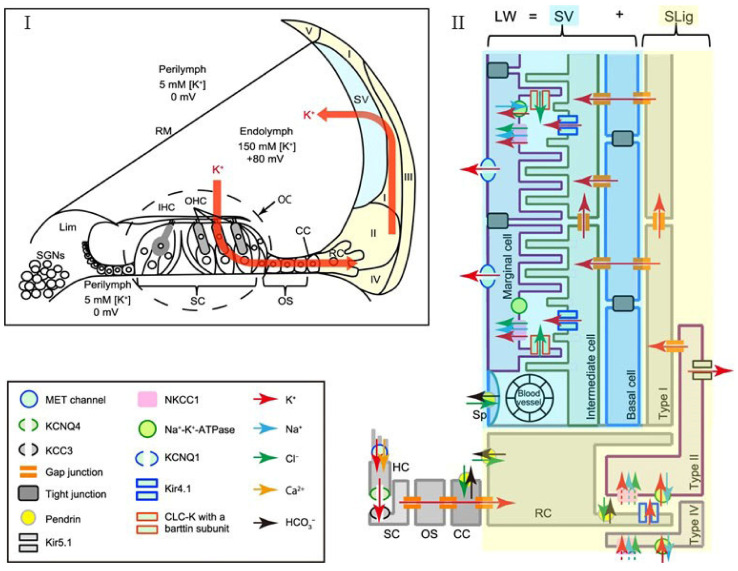
Figure 2.
Diagram depicting Na,K-ATPAse, NKCC1 ion transporters, and K+ channels involved in ion circulation in the cochlear lateral wall. (I) Recirculation of K+ between the HCs into the endolymph of the scala media during auditory transduction. The ion channels involved in K+ recycling play a vital role in generating the EP and maintaining the lymphatic homeostasis needed for normal hearing. (II) NKCC1, Na,K-ATPase, KCNQ1, KCNQ4, Kir 4.1, Kir 5.1, and KCC3 are some various ion transporter channels that play a role in K+ circulation and endocochlear potential generation in the SV. HC: hair cells; IHC: inner hair cells; OHC: outer hair cells; OC: organ of Corti; SC: supporting cells; OS: outer sulcus cells; CC: Claudius cells; RC: root cells; Lim: spiral limbus; RM: Reissner’s membrane; SLig: spiral ligament; Sp: spindle cell. From Watabe et al. [108] (Figure 1), with permission from the publisher.