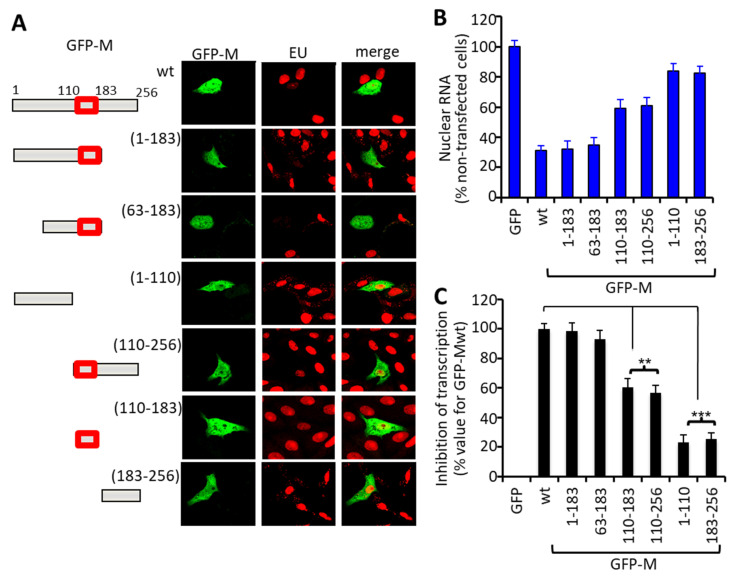
Figure 2.
The central nucleotide binding region of RSV M is sufficient to effect transcriptional inhibition in living cells. (A) Schematic representations of the GFP-M fusion constructs used (left). Numbers refer to the M amino acid sequence, with the central domain, including the RNA binding region and nuclear localization signal (NLS), shown as a red box. Representative CLSM images of Vero cells expressing GFP-Mwt or truncated derivatives thereof (right) treated with EU, fixed, permeabilized, and stained for de novo synthesized RNA as per the legend to Figure 1. (B) Quantitative analysis for inhibition of de novo RNA synthesis (n = 15) as per the legend to Figure 1. (C) Results from (B) are expressed in terms of percent inhibition of transcription relative to that effected by GFP-Mwt. Significant differences are indicated, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.