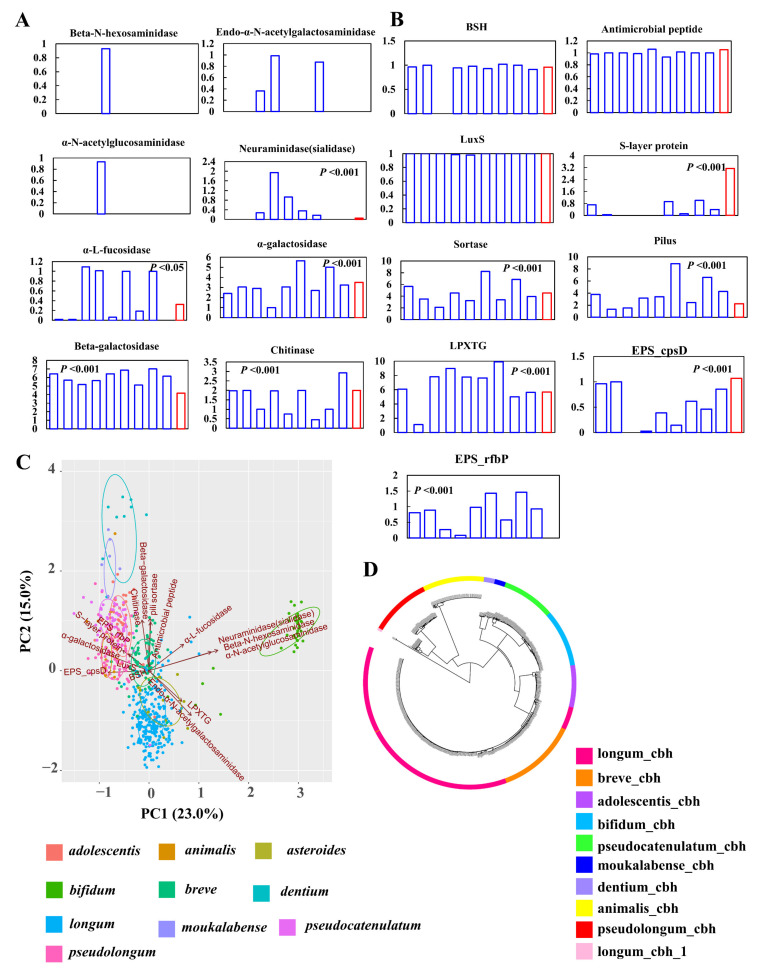
Figure 7.
Distribution of probiotic effector molecules among B. pseudolongum and other Bifidobacterium species. (A) Average gene numbers of mucin-glycan foraging enzymes per strain by Bifidobacterium species. Each column represents a bifidobacterial species. From left to right: B. adolescentis, B. animalis, B. asteroides, B. bifidum, B. breve, B. dentium, B. longum, B. moukalabense, B. pseudocatenulatum, and B. pseudolongum. (B) Average gene numbers of probiotic effectors per strain for each species. Each column represents a bifidobacterial species. From left to right: B. adolescentis, B. animalis, B. asteroides, B. bifidum, B. breve, B. dentium, B. longum, B. moukalabense, B. pseudocatenulatum, and B. pseudolongum. (C) PCA plot of the strains from different Bifidobacterium species by taking the numbers of each included probiotic effector as inputs. (D) Phylotypes of BSH sequences by Bifidobacterium species. The BSH reference sequences were removed after evaluating the BSH types. The information for all the used BSH sequences are listed in Table S2. The Bifidobacterium species with more than 10 publicly available sequenced genomes in the NCBI database were analyzed (including 786 strains). Statistical analyses were performed between B. pseudolongum strains and the strains of the other studied bifidobacterial species.