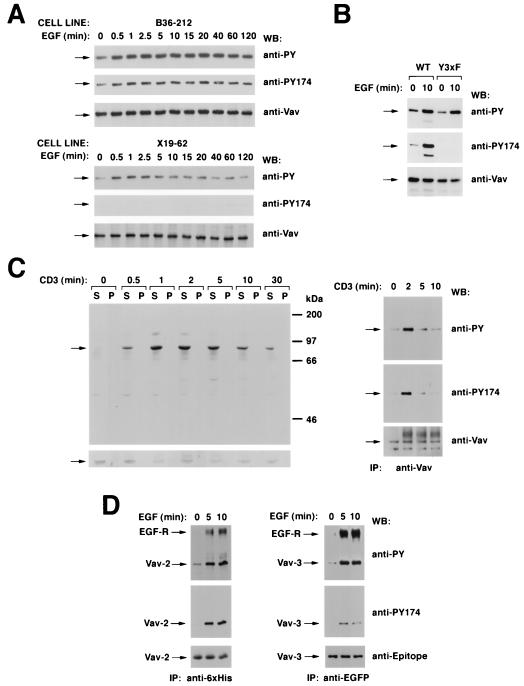
FIG. 9.
(A) Phosphorylation of residue Y174 by EGF and specificity of the antibodies to Vav phosphorylated at that position. NIH 3T3 cell clones expressing either wild-type Vav (B36-212 cells; top) or Vav Y3xF (X19-62 cells; bottom) were serum starved for 48 h and then stimulated with EGF for the indicated periods of time. After stimulation, cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-Vav antibodies and immunocomplexes were subjected sequentially to Western blotting (WB) with antiphosphotyrosine (anti-PY) antibodies, the phosphospecific antibody to residue Y174 of Vav (anti-PY174), and anti-Vav antibodies. Arrows, migration of Vav proteins. (B) Specificity of anti-VavPY174 antibodies in COS-1 cells. Quiescent and EGF-stimulated COS-1 cells expressing the indicated Vav proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Vav antibodies and then subjected sequentially to Western blotting with anti-VavPY174, anti-Vav, and antiphosphotyrosine antibodies. WT, wild type. (C) Phosphorylation of Y174 in T cells. (Left) Jurkat cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 antibodies for the indicated periods of time and lysed, and equivalent amounts of total cellular lysates from the Triton X-100-soluble (S) and -insoluble (P) fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-VavPY174 (top) or anti-Vav (bottom) antibodies. (Right) Vav proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) from Jurkat cells stimulated for the indicated periods of time with anti-CD3 and then subjected sequentially to Western blot analysis with antibodies as listed for panel A. Arrows, migration of Vav. (D) Phosphorylation of the position equivalent to Y174 in Vav-2 (residue Y172) and Vav-3 (residue Y173). COS-1 cells expressing ectopically six-His-tagged Vav-2 (left) and EGFP-tagged Vav-3 (right) were serum starved overnight and stimulated for the indicated periods of time with EGF. After stimulation, cells were lysed and Vav family proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-polyhistidine (Vav-2; left) or anti-EGFP (Vav-3; right) antibodies. Washed immunocomplexes were then subjected to sequential Western blot analysis with antiphosphotyrosine, anti-VavY174, and the respective antiepitope antibody. For panel A, signals were developed either using 125I-labeled protein A (anti-Vav immunoblots) or by treatment with an anti-mouse immunoglobulin G antibody followed by incubations with 125I-labeled protein A (antiphosphotyrosine) or by the ECL method (anti-VavPY174). For panels B and C, signals were developed using only the ECL method.