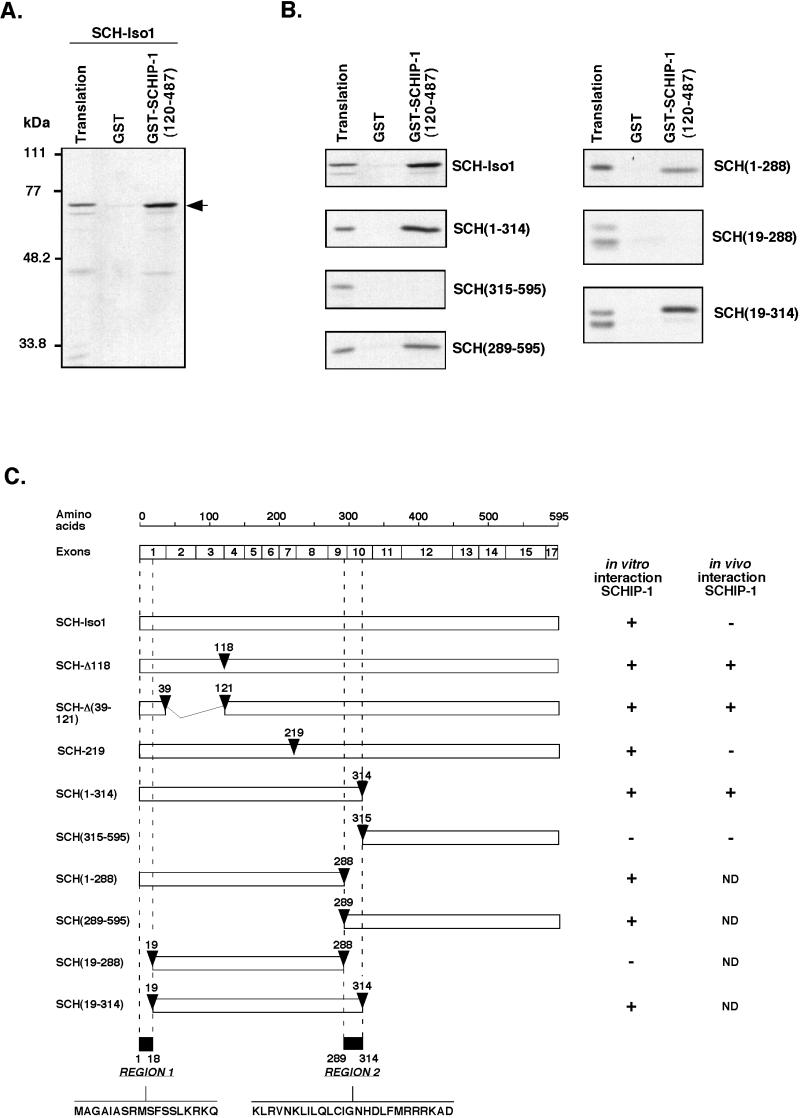
FIG. 4.
SCHIP-1 interacts with two distinct regions of schwannomin in vitro. (A and B) In vitro interaction of schwannomin with SCHIP-1. Either GST or GST–SCHIP-1(120-487) was bound to glutathione-agarose beads and incubated in TKT40 buffer with [35S]methionine-labeled SCH-Iso1 or deletion mutants SCH(1-314), SCH(315-595), SCH(289-595), SCH(1-288), SCH(19-288), and SCH(19-314) as indicated. After washing, retained schwannomin and schwannomin variant proteins were eluted, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. Aliquots of the labeled proteins corresponding to 1/40 of the input were loaded on the same gel (Translation). SCHIP-1 interacts with SCH-Iso1 in vitro (A). This interaction requires two regions of schwannomin spanning amino acids 1 to 18 and 289 to 314 (B). (C) Map of schwannomin constructs and summary of the properties of the corresponding proteins. (Left) Map of schwannomin constructs. Open boxes indicate the regions of schwannomin that are encoded by the different constructs. Positions of the truncations or amino acids substitutions and deletions are shown by arrowheads. The two regions found to be implicated in the interaction with SCHIP-1 are indicated at the bottom. Relative positions of the NF2 exons and schwannomin amino acid residues are illustrated on the top. (Right) Summary of properties of the various proteins. In the two columns are indicated the ability of the various proteins to interact in GST pull-down experiments with SCHIP-1 (column 1) and the ability of the various proteins to coimmunoprecipitate with SCHIP-1 when the proteins are overexpressed in HeLa cells (column 2). +, interaction in vitro or coimmunoprecipitation detected; −, interaction in vitro or coimmunoprecipitation not detected; ND, ability to coimmunoprecipitate not determined.