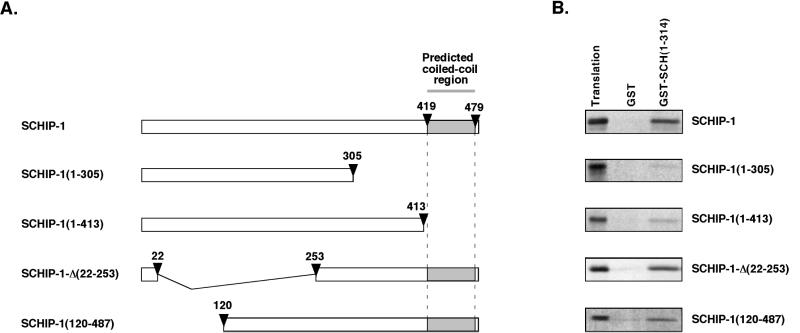
FIG. 6.
The coiled-coil region of SCHIP-1 is required for efficient interaction with schwannomin in vitro. (A) Map of SCHIP-1 constructs. Open boxes indicate the regions of SCHIP-1 encoded by the different constructs. The grey color highlights the localization of the coiled-coil domain. Arrowheads indicate the amino acids delimiting the coiled-coil domain and the positions of truncations and deletions. (B) In vitro interaction of SCHIP-1 with schwannomin. Either GST or GST–SCH(1-314) was bound to glutathione-agarose beads and incubated in TKT150 buffer with [35S]methionine-labeled full-length SCHIP-1, SCHIP-1(1-413), SCHIP-1(1-305), SCHIP-1-Δ(22-253), or SCHIP-1(120-487) as indicated. After washing, retained SCHIP-1 and SCHIP-1 variants were eluted and visualized by autoradiography. Aliquots of the labeled proteins corresponding to 1/40 of the input were loaded on the same gel (Translation). Schwannomin interacts in vitro with full-length SCHIP-1 or SCHIP-1 proteins deleted in the N-terminal domain [SCHIP-1-Δ(22-253) and SCHIP-1(120-487)] but not or poorly with truncated SCHIP-1 proteins missing the coiled-coil region [SCHIP-1(1-413) and SCHIP-1(1-305)].