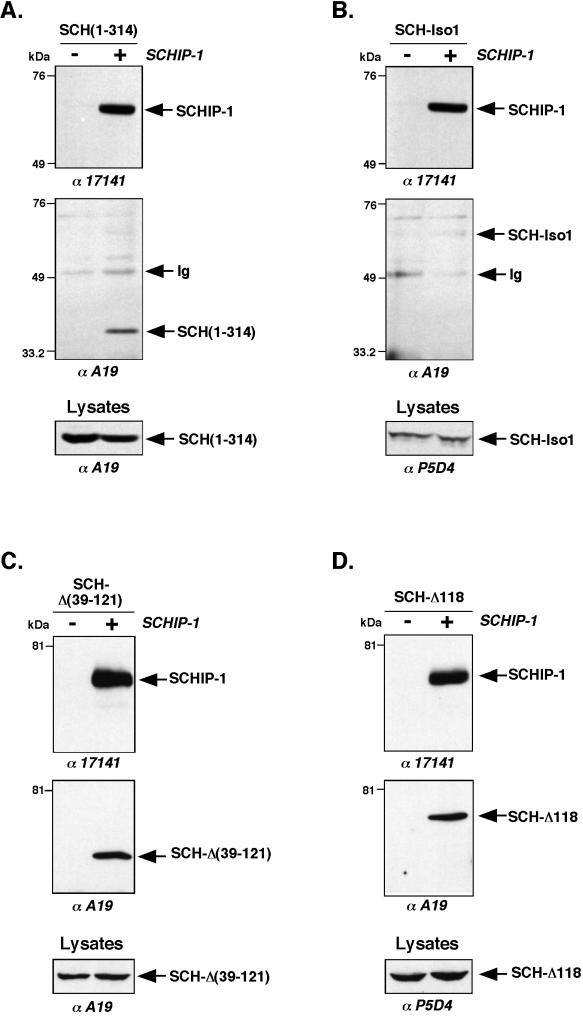
FIG. 7.
In vivo interaction of schwannomin and SCHIP-1. HeLa cells were cotransfected with either pCB6-HA-SCHIP-1 expression vector (+) or empty pCB6 vector (−) and vector expressing schwannomin variants SCH(1-314) (A), SCH-Iso1 (B), SCH-Δ(39-121) (C), and SCH-Δ118 (D). Twenty-four hours after transfection, proteins extracts were prepared as described in Materials and Methods, and coimmunoprecipitations were performed with the anti-HA MAb 12CA5. Precipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE on an 8% gel, electroblotted, and submitted to two rounds of immunoblotting, first with the anti-SCH polyclonal antibody A19 and then with the anti-SCHIP-1 polyclonal antibody 17141. Twenty microliters of crude protein extract (Lysates) was also subjected to immunoblotting with either the anti-SCH polyclonal antibody A19 or the anti-VSV monoclonal antibody MAb P5D4, to verify expression of schwannomin proteins. Antibodies used for Western blotting are indicated below the gels. SCHIP-1 is able to associate in vivo with the schwannomin variant SCH(1-314) (A) and the two naturally occurring mutants SCH-Δ(39-121) and SCH-Δ118 (C and D) but not with SCH-Iso1 (B).