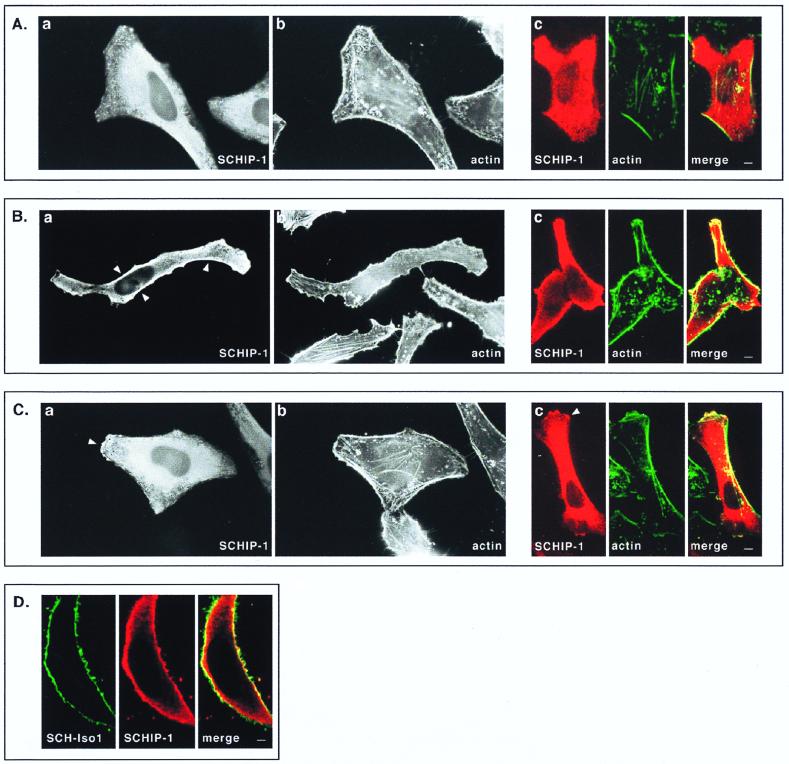
FIG. 8.
Colocalization of SCHIP-1 and schwannomin in overexpressing cells. HeLa cells were transfected with expression vector pCB6-HA-SCHIP-1 alone (A to C) or together with an SCH-Iso1 expression vector (D). Twenty-four hours later, cells were processed for indirect immunofluorescence using MAb 12CA5 to detect the HA-tagged SCHIP-1 protein (A to D), FITC-phalloidin to reveal F-actin (A to C), and the C14 rabbit polyclonal antibody to detect schwannomin (D). Coverslips were examined with a Leica epifluorescence microscope (A to C, views a and b) and with a Leica confocal microscope (A to C, views c; D). Red indicates anti-mouse secondary antibody staining (SCHIP-1) (A to D), whereas green represents actin staining (A to C) or anti-rabbit secondary antibody staining (schwannomin) (D). Overlays are shown with yellow indicating colocalization (A to D). (A to C) Representative examples of the three main types of localization that have been observed for SCHIP-1 on a single coverslips. Arrowheads indicate regions where SCHIP-1 localizes below the cytoplasmic membrane (B) or colocalizes with cortical actin (C). (D) Cell in which SCHIP-1 localizes beneath the cytoplasmic membrane and colocalizes partially with SCH-Iso1. Scale bars, 5 μm (A to C) and 2 μm (D).