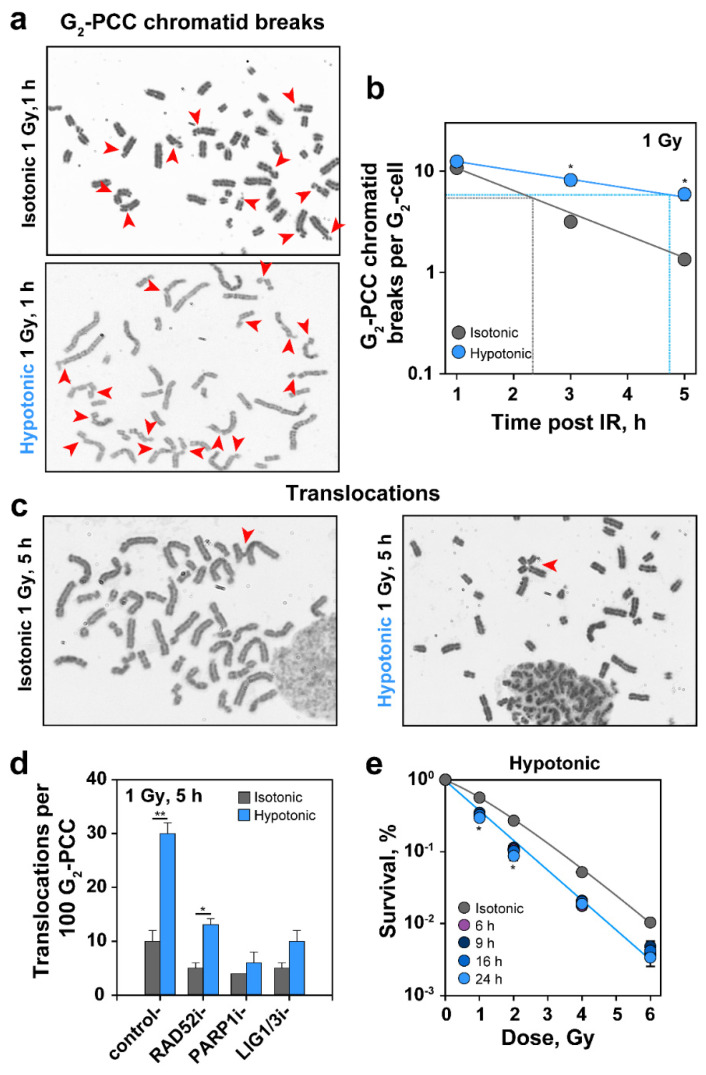
Figure 7.
HypoS suppresses repair of interphase chromosome breaks, increases translocation formation and sensitizes cells to IR-induced killing. (a) RPE cells were incubated in isotonic or hypotonic medium after IR. G2-PCCs showing chromatid breaks (indicated by arrows) at 1 h after exposure to 1 Gy. (b) Kinetics of PCC break repair in cells exposed to 1 Gy and treated isotonically or hypotonically. Dotted lines indicate 50% chromatid break rejoining. Means ± SE are calculated from two experiments. Error bars are visible when larger than the symbols used. (c) Translocation formation in RPE cells exposed to 1 Gy and treated isotonically or hypotonically before processing for PCC. G2-PCCs at 5 h after exposure to 1 Gy showing translocations (indicated by arrows). (d) Quantification of translocations in cells treated with DMSO (control), RAD52 inhibitor (6-OH-DOPA, 10 µM), PARP1 inhibitor (PJ34, 5 µM), Ligase 1 and 3 inhibitor (L67, 50 µM), at 5 h after exposure to 1 Gy. Means ± SE are calculated from two independent experiments. (e) Clonogenic survival of isotonically and hypotonically treated RPE cells. Incubation in hypotonic medium after IR was carried out for 6, 9, 16 and 24 h (visible when the symbols are not overlapping). Means and SE are calculated from four determinations in two experiments. Error bars are visible when larger than the symbols used. For all plots, the significance of differences between individual measurements under isotonic and hypotonic conditions is indicated by the asterisk: * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 (in (e) only if valid for all time points).