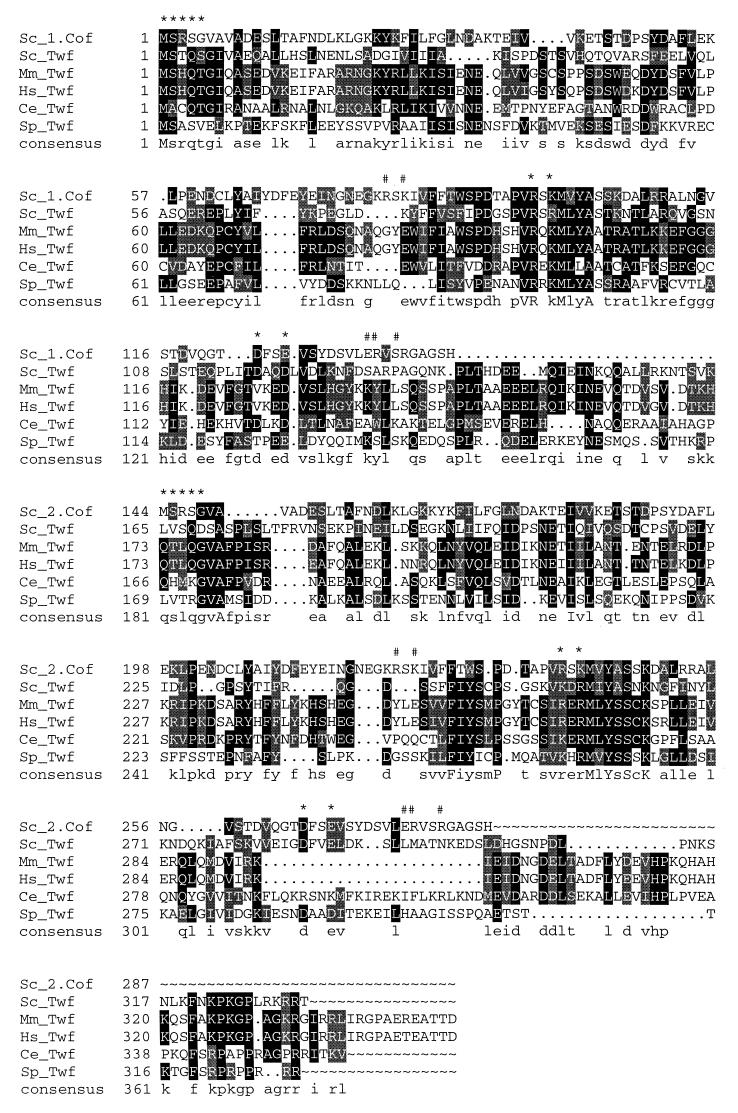
FIG. 1.
Sequence alignment of S. cerevisiae (Sc), human (Hs), mouse (Mm), C. elegans (Ce), and S. pombe (Sp) A6/twinfilin proteins. Residues either identical or similar to yeast twinfilin (Twf) are highlighted with black or grey, respectively. Yeast cofilin (Sc_1.Cof and Sc_2.Cof) is included into this sequence alignment to bring mutagenesis and structural data of cofilin into alignment. Residues that have been shown to be important for F-actin binding in yeast cofilin (13) are indicated above the sequences (#), as are the residues that have been shown to be important for both G- and F-actin binding in yeast cofilin (∗). A linker region approximately 30 residues in length is clearly observed between the two cofilin-like regions (ADF-H domains) in A6/twinfilins. This linker region contains a conserved proline followed by up to three conserved negatively charged residues, indicating that it may also have more specific biological function(s). Protein names and accession numbers for the sequences are as follows (where no database is stated, the accession number refers to GenBank): S. cerevisiae cofilin, Q03048 (Swissprot); S. cerevisiae twinfilin, YGR080W (SGD); Mus musculus twinfilin, U82324; Homo sapiens twinfilin, A55922 (PIR); C. elegans twinfilin: U46668 (ID, g1166579); S. pombe twinfilin, AL034490 (ID, g4008554). The software used were PileUp and LineUp in the Genetics Computer Group Wisconsin Package together with Boxshade 3.21.