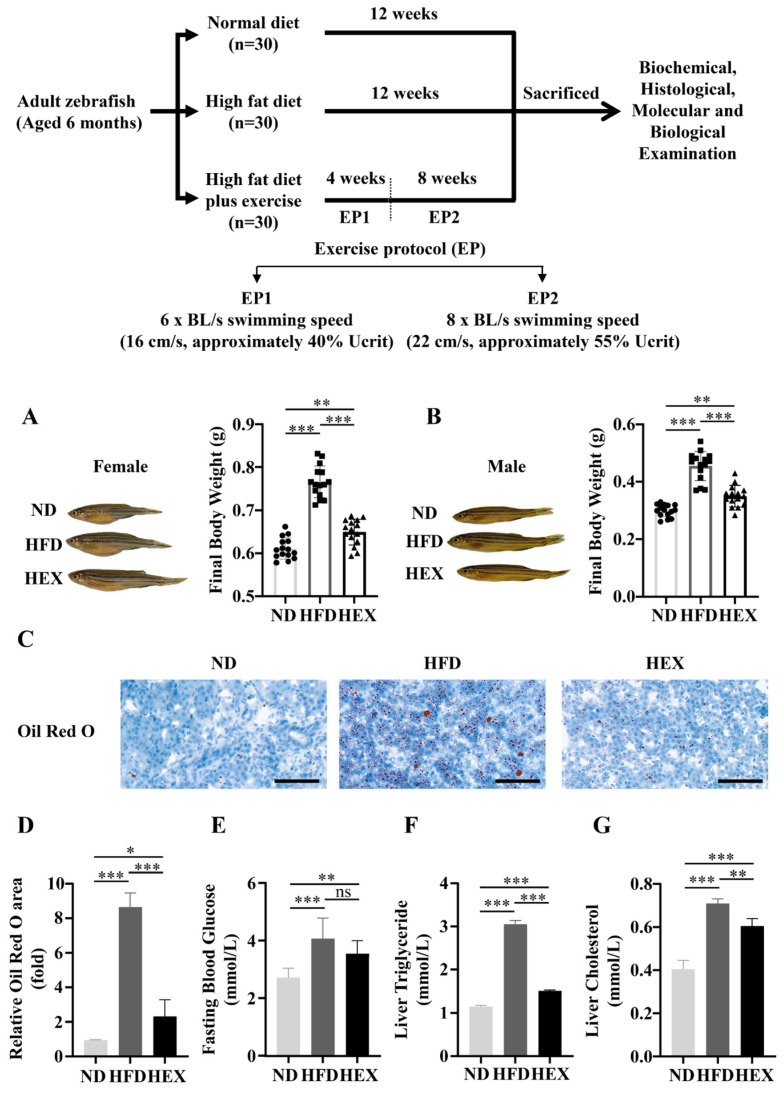
Figure 1.
Zebrafish receiving a high exercise regimen (HEX) had reduced body weight gain and lipid accumulation compared to high-fat diet (HFD) zebrafish. Normal diet (ND) zebrafish represent the control group. (A,B) Morphology and body weight of zebrafish. (C) Oil Red O staining of zebrafish livers (n = 3). (D) Quantitation of Oil Red O staining. (E) Fasting blood glucose (ND, n = 13; HFD, n = 10; HEX, n = 11). (F) Liver triglyceride (n = 5). (G) Liver cholesterol (n = 5). The above experiments were carried out using 9-month-old zebrafish. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001. Data represent the mean, and error bars represent SEM. Scale bar, 20 μm. NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ND, normal diet; HFD, high fat diet; HEX, high-fat diet plus exercise.