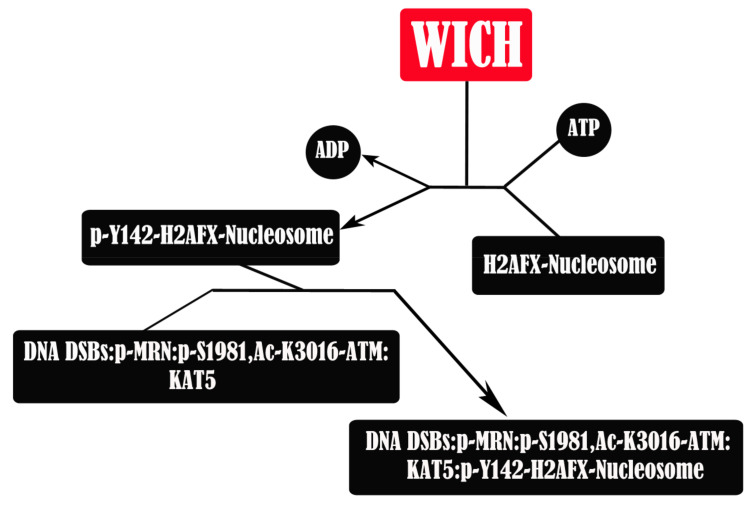
Figure 8.
BAZ1B is involved in the recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA DSBs. It phosphorylates H2AF on Tyr142. After DNA DSB induction, the MRN complex (Mre11, Rad50, and Nbs1) binds to the DNA breaks followed by ATM recruitment. ATM, in dimeric form, is in a complex with KAT5. KAT5 then acetylates ATM at DNA DSB. MRN activates ATM dimer by promoting its dissociation into monomers and then ATM phosphorylates the NBN (Nbs1) component of the MRN complex, resulting in the p-MRN:p-S1981,Ac-K3016-ATM:KAT5 protein complex at DNA DSB sites. This complex then recognizes and associates with the p-Y142-H2AFX-nucleosome. Phosphorylation of Ser139 and dephosphorylation of Tyr142 are the following steps. This nucleosomal complex will then undergo multiple modifications such as phosphorylation, methylation, and ubiquitination as well as binding of additional proteins and will eventually lead into nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) and homology-dependent repair through homologous recombination repair (HRR) or single strand annealing (SSA).