Figure 2.
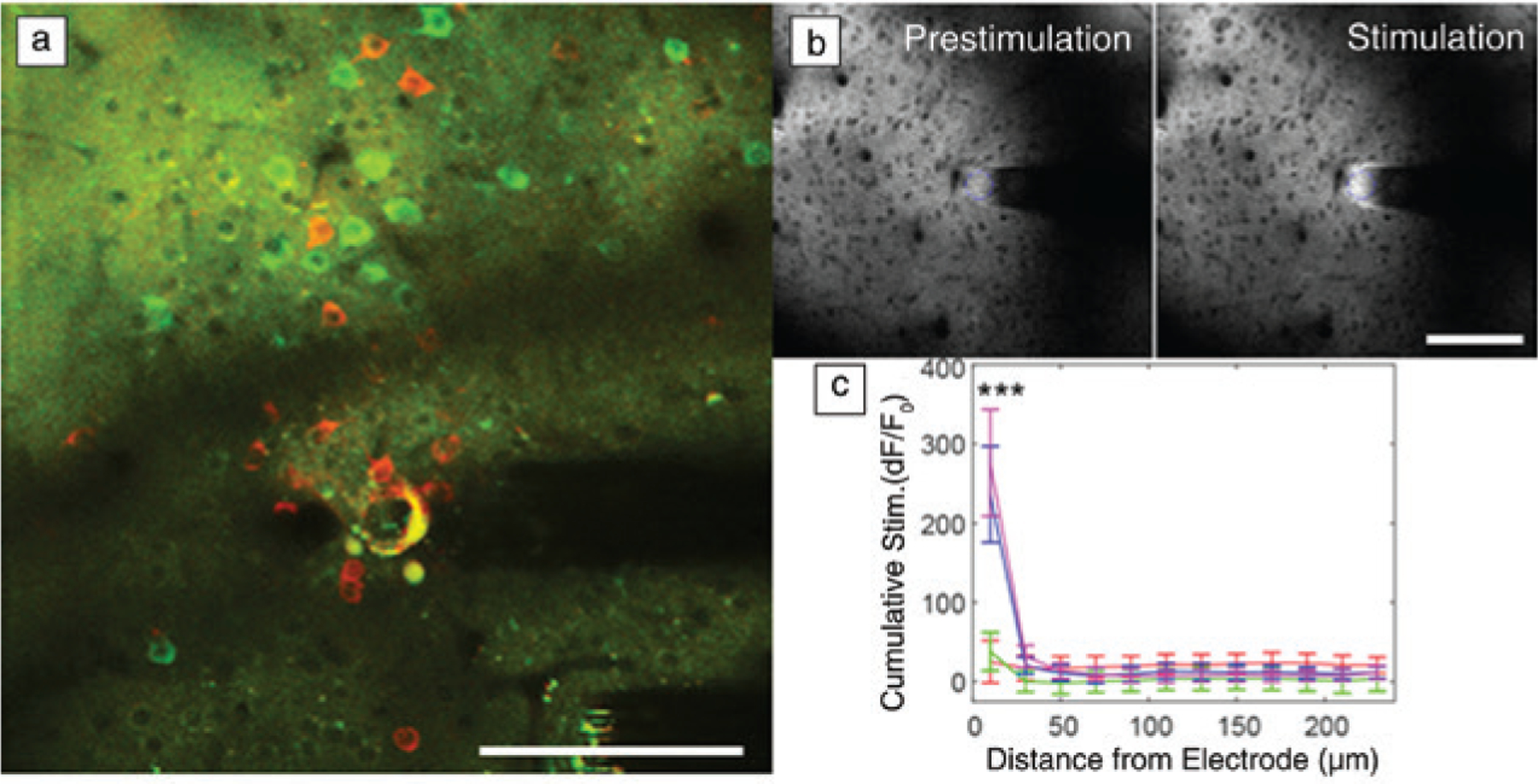
Functional neural activity near implanted recording and stimulation interfaces are sensitive to distance. (a) In vivo two-photon microscopy (TPM) of neurons in the visual cortex show GCaMP activity (green; a chimera protein of green fluorescent protein [GFP], calmodulin, and M13, a peptide sequence from myosin light chain kinase) at a distance (>60 μm) a month after chronic implantation. However, there are silenced neurons (red) near the electrode that can only be driven by strong microstimulation. (b) In vivo TPM of extracellular glutamate measured by iGluSnFr (intensity-based glutamate sensing fluorescent reporter) before and after electrical stimulation shows that significant glutamate release from electrical stimulation is limited to the first 20 μm. (c) These studies indicate that biomaterial selection and probe designs for maintaining a tightly coupled functional interface are crucial for both recording and stimulating interfaces. Scale bar = 100 μm. (b, c) Reprinted with permission from Reference 65. © 2020 Elsevier.
