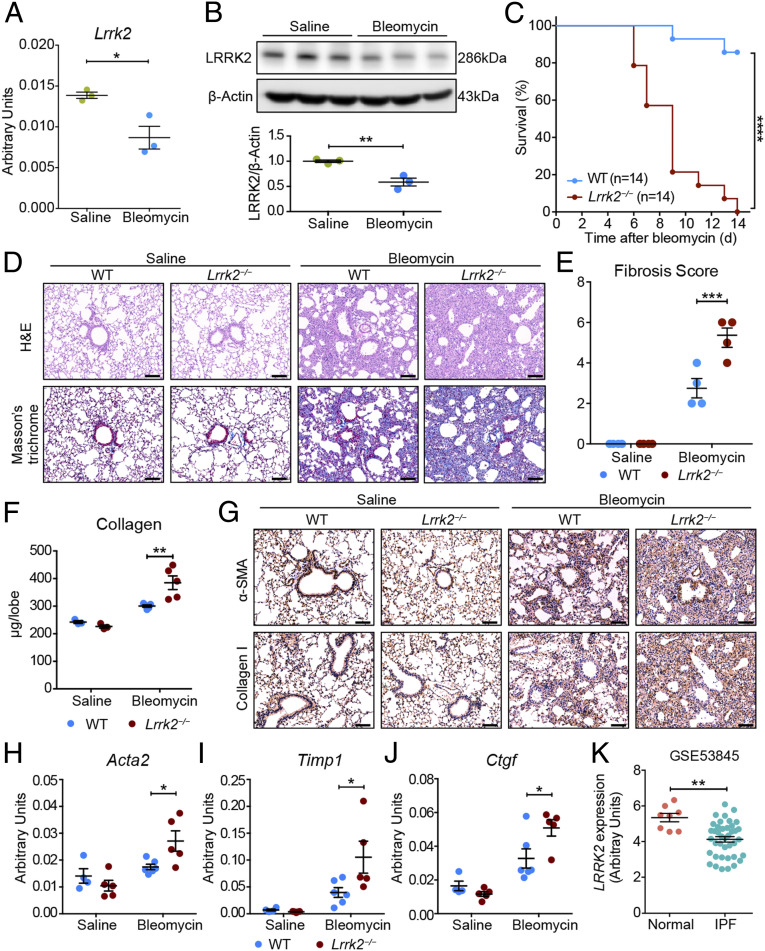
Fig. 1.
LRRK2 expression was down-regulated in fibrotic lungs, and its deficiency in mice exacerbated pulmonary fibrosis. (A and B) Quantitative analyses of (A) Lrrk2 mRNA by qRT-PCR and (B) LRRK2 protein by Western blot in lung tissues of WT male mice after saline or 1.5 mg/kg bleomycin treatment for 10 d (n = 3 mice per group). (C) Survival curves of bleomycin-treated WT and Lrrk2−/− male mice were recorded over a 14-d period (n = 14 mice per group); ****P < 0.0001, by log-rank test. (D–J) WT and Lrrk2−/− male mice were challenged with saline or bleomycin for 10 d (n = 3 to 6 mice per group). (D) Representative images of the H&E- and Masson’s trichrome–stained lung sections. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (E) Fibrosis score based on stained lung sections from saline or bleomycin-treated groups. (F) Quantification of collagen content in lung homogenates using the Sircol Assay. (G) Representative immunohistochemical analysis of α-SMA and Collagen I in lung sections. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) Quantitative analyses of mRNA expression of indicated profibrotic genes including (H) Acta2, (I) Timp1, and (J) Ctgf in lung tissues by qRT-PCR. (K) LRRK2 mRNA expression in lung samples of IPF patients (n = 40) compared with normal controls (n = 8) based on the reanalysis of a published dataset (GSE53845) (24). Data in A, B, E, F, and H–J are representative of two to three independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t test (A, B, K) and two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (E, F, H–J).