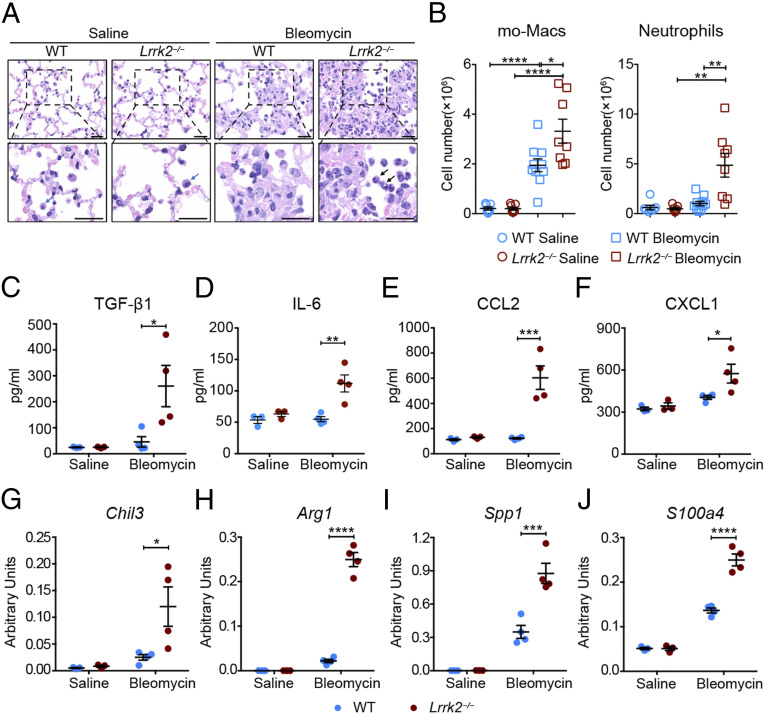
Fig. 2.
LRRK2 deficiency led to enhanced profibrotic immune responses and promoted the profibrotic polarization of mo-Macs in the development of pulmonary fibrosis. WT and Lrrk2−/− male mice were challenged with saline or 1.5 mg/kg bleomycin for 7 d. (A) Representative images of H&E-stained lung sections; blue arrow: alveolar macrophage; black arrow: neutrophil. (Scale bars: 20 µm.) (B) Flow cytometric analysis and quantification of mo-Macs and neutrophils in enzymatically digested whole lung tissues from saline- or bleomycin-treated WT and Lrrk2−/− mice (n = 7 to 10 mice per group). (C–F) ELISA analysis of (C) TGF-β1, (D) IL-6, (E) CCL2, and (F) CXCL1 levels in BALF from WT and Lrrk2−/− mice (n = 3 to 4 mice per group). (G–J) Quantification of mRNA levels of profibrotic factors, including (G) Chil3, (H) Arg1, (I) Spp1, and (J) S100a4, by qRT-PCR in isolated lung mo-Macs (n = 3 to 4 mice per group). Data are shown as mean ± SEM and are (B) integrated from three independent experiments or (C–J) representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, by (B) two-tailed Student’s t test or (C–J) two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test.