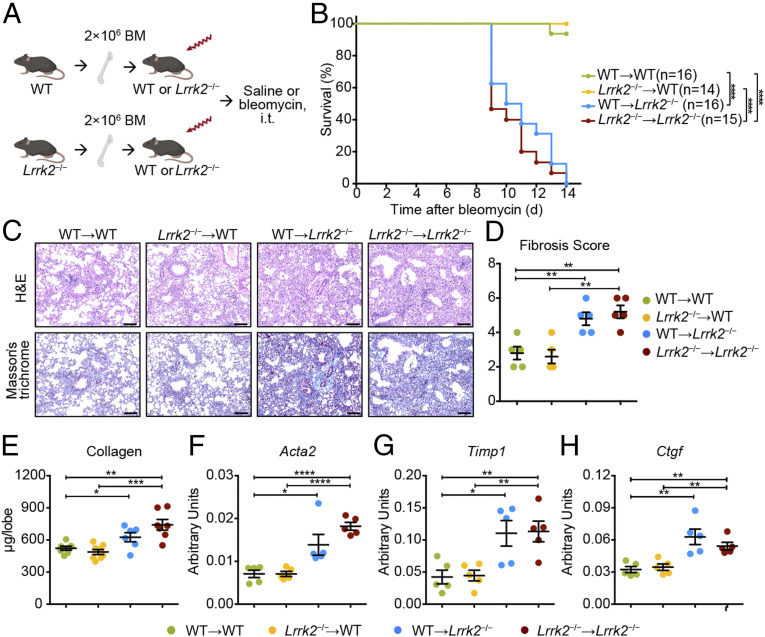
Fig. 3.
LRRK2 deficiency in nonhematopoietic cells accounted for the enhanced severity to bleomycin-mediated fibrosis. (A) Scheme of BM chimeric mice construction and experimental design. Icons were created with BioRender.com. (B) Survival curves of mice from the four groups of BM chimeric mice treated with 1.5 mg/kg bleomycin (n = 14 to 16 mice per group) were recorded over a 14-d period; ****P < 0.0001 by log-rank test. (C–H) Lung tissues from bleomycin-treated BM chimeric mice (n = 5 to 6 mice per group) were harvested at day 10 for the following analyses. (C) Representative images of H&E- and Masson’s trichrome–stained lung tissue sections. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (D) Fibrosis scores based on stained lung sections. (E) Quantification of collagen content in lung homogenates using the Sircol Assay. Quantitative analyses of mRNA levels of indicated fibrosis-associated genes, including (F) Acta2, (G) Timp1, and (H) Ctgf, by qRT-PCR in lung tissues from indicated BM chimeric mice after bleomycin challenge. Data in D–H are shown as mean ± SEM and are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, by two-tailed Student’s t test.