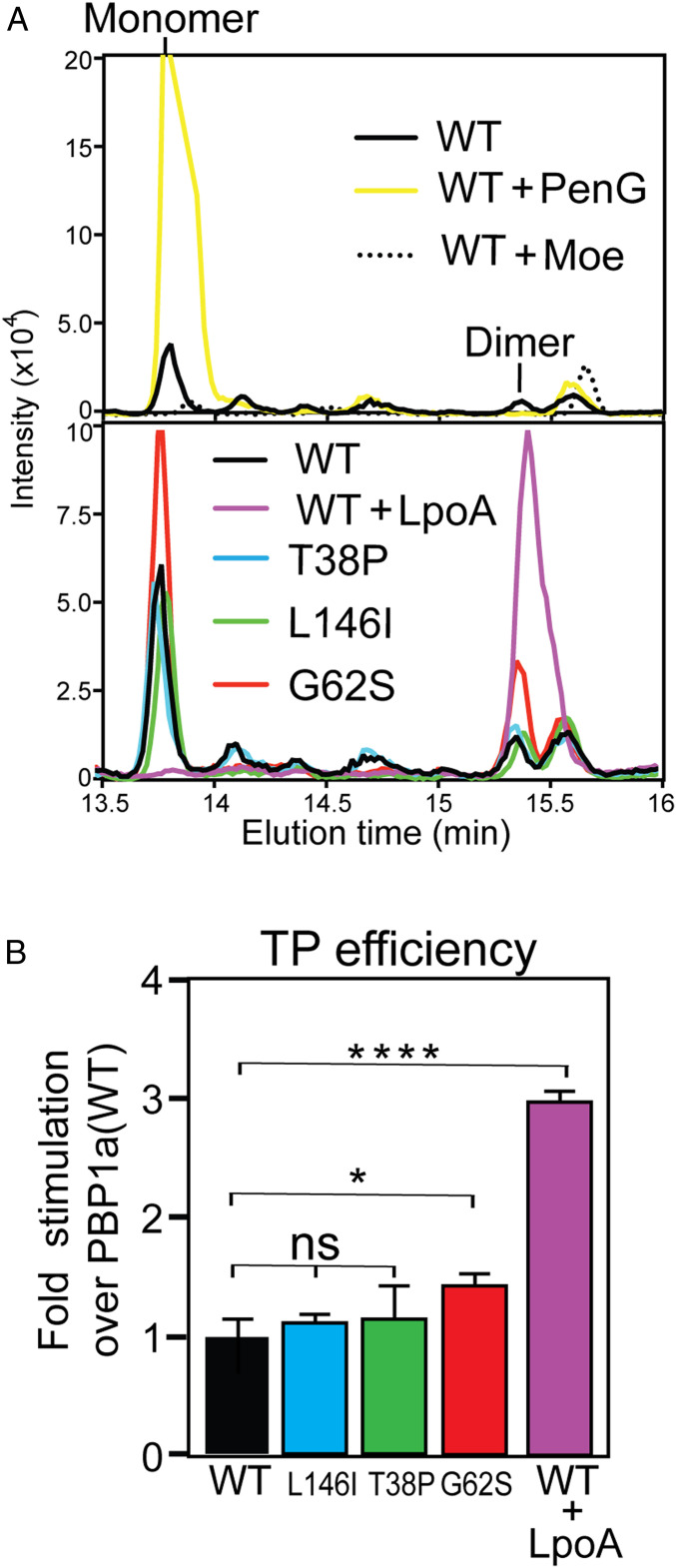
Fig. 4.
E. coli PBP1a* variants are not strongly activated for TPase function. (A) Shown are extracted ion LC-MS chromatograms of mutanolysin-treated products from PG synthesis reactions with E. coli lipid II (200 µM) and purified PBP1a(WT) or its PBP1a* derivatives (5 µM) incubated at 25 °C for 5 min prior to heat inactivation. The Upper panel compares representative traces from PBP1a(WT) without or with penG (50 µM) or moenomycin (50 µM) treatment as indicated. The Lower panel compares representative traces from reactions with PBP1a(WT) and its indicated PBP1a* derivatives as well as PBP1a(WT) with added LpoA (10 µM). All traces are averages of three to five independent reactions for each condition/protein variant. (B) The PG cross-linking efficiency in each of the reactions was calculated by dividing the amount of dimer formed by the total PG produced (monomer + dimer). Results are averages of three experiments. Error bars represent the SEM value. Unpaired Student’s t test was used to determine whether the responses of the cells to the treatment was significantly different (ns, not significant P > 0.05, *P ≤ 0.05, ****P ≤ 0.0001).