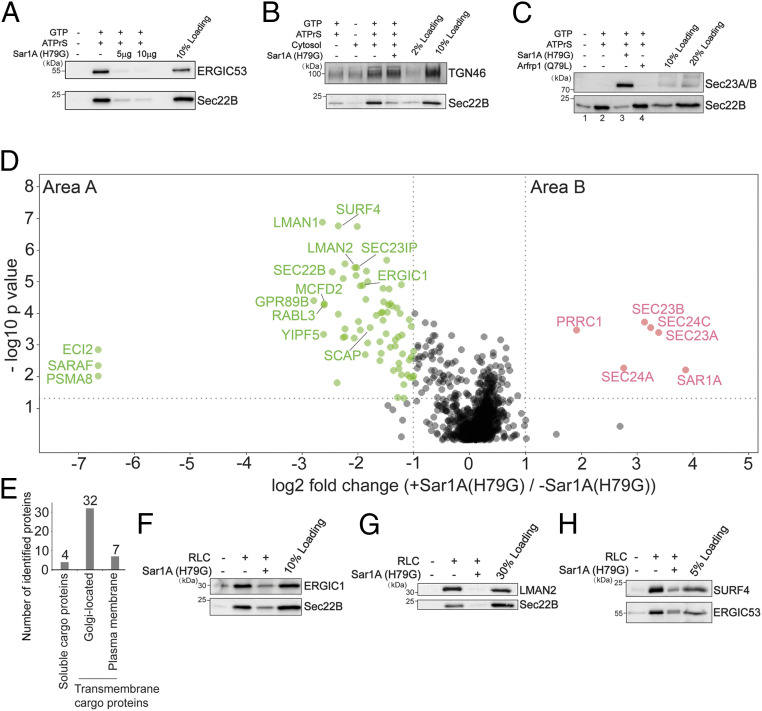
Fig. 4.
Identification of cargo proteins and cytosolic proteins that are dependent on Sar1A to be associated with transport vesicles. (A–C) The vesicle formation assay was performed using the indicated reagents. Vesicle fractions were analyzed by immunoblot. (D) The vesicle formation assay was performed in the presence or absence of Sar1A(H79G). The isolated vesicles in each experimental group were resuspended in RapiGest SF surfactant. The proteins in the vesicle fractions were trypsin digested and analyzed by label-free mass spectrometry. The log2 ratio of the abundance of each identified protein in the vesicles prepared in the presence of Sar1A(H79G) over that in the vesicles prepared in the absence of Sar1A(H79G) was plotted on the x axis and the −log10 P value of the difference was plotted on the y axis. (E) Number of proteins identified in area A in D categorized based on predictions from Uniprot. (F–H) The vesicle formation assay was performed using the indicated reagents. The vesicle fraction was analyzed by immunoblot. Data shown in A–C and F–H are representative examples of three biological repeats.