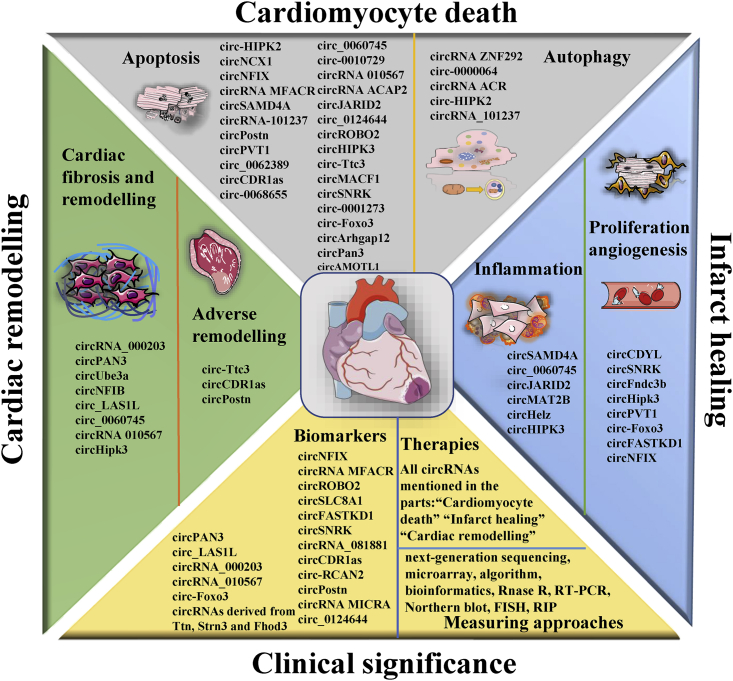
Figure 6.
The biological functions and clinical significances of circRNAs for MI
circRNAs, which can be measured by various approaches in MI patients, tissues, and cells, significantly participate in regulation of the cellular processes and the pathophysiology of MI and have excellent biological functions and clinical significances for MI. Considerable circRNAs are involved in cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy, inflammation, proliferation and angiogenesis, cardiac remodeling, and fibrosis, providing novel diagnostic and treatment strategies for MI.