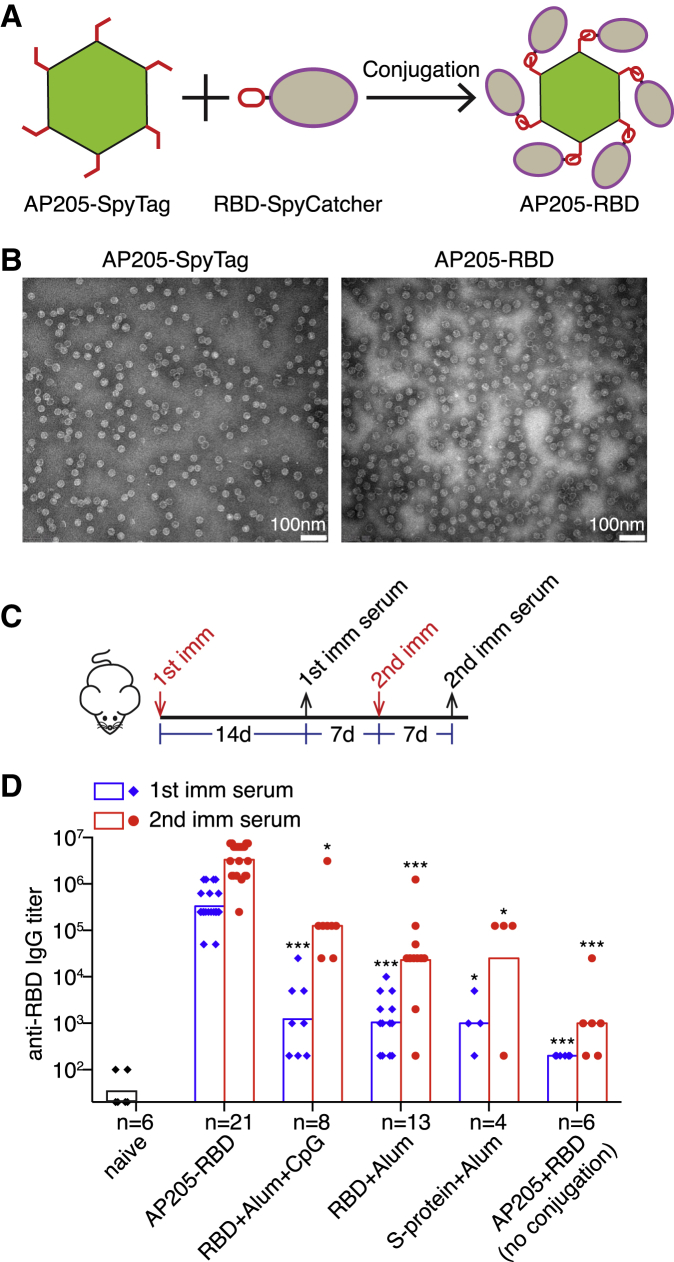
Figure 1.
AP205-RBD elicited high titers of anti-RBD antibody in mice
(A) Construction strategy of AP205-RBD. Purified AP205-SpyTag and RBD-SpyCatcher are mixed in vitro to form the SpyTag:SpyCatcher covalent bond.
(B) Transmission EM images of intact AP205-SpyTag and AP205-RBD.
(C) Time points for the first (1st) and second (2nd) immunization (imm) and serum collection in mice.
(D) Serum anti-RBD IgG from mice immunized with the indicated antigens was measured by ELISA. Endpoint titers were presented. Symbols indicate data collected from individual mice. Bars indicate the geometric mean of each group. The number (n) of mice examined in each group was shown. Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare the five immunized groups within either the “1st imm serum” or the “2nd imm serum.” There are significant differences among the five groups for both the “1st” and the “2nd imm serum.” Dunn’s multiple comparisons test was then used to compare between the AP205-RBD-immunized group and one of the other immunized groups, and the adjusted p value was used to determine the statistical significance and indicated in the graph (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
See also Figure S1.