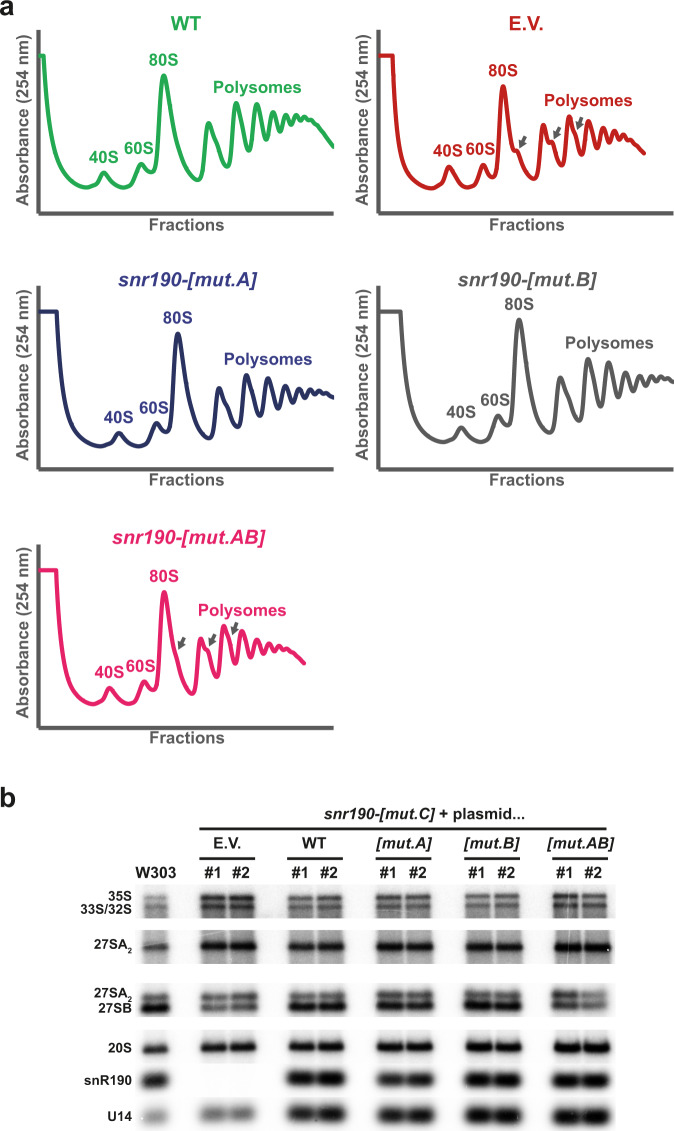
Fig. 4. snR190 boxes A and B are required for its function in LSU synthesis.
a Polysome profiles on sucrose gradients of W303 snr190-[mut.C] strain transformed with vectors supporting expression of wild-type snR190 (WT, green) or bearing mutations in its antisense elements box A (snr190-[mut.A], dark blue), box B (snr190-[mut.B], grey) or both (snr190-[mut.AB], pink), or with the empty vector as control (E.V., red). Cell extracts were prepared and analyzed as in Fig. 2c. b Steady-state levels of distinct pre-rRNAs and U14 and snR190 snoRNAs in isogenic wild-type and snr190-[mut.C] strains in the W303 background; cells were transformed with plasmids supporting expression of wild-type snR190 (WT) or bearing mutations in its antisense elements box A ([mut.A]), box B ([mut.B]) or both ([mut.AB]), or with the empty vector as control (E.V.). Experiments were performed as explained in the legend of Fig. 2b. Note: the first five lanes of this figure are identical to those presented in Fig. 2b, where they were used to support the conclusion that ectopic re-expression of snR190 restores pre-rRNA processing in the snr190-[mut.C] strain. This experiment was performed once with each independent clone for the W303 background and twice with each independent clone for the BY4741 background (see also Supplementary Fig. 8).