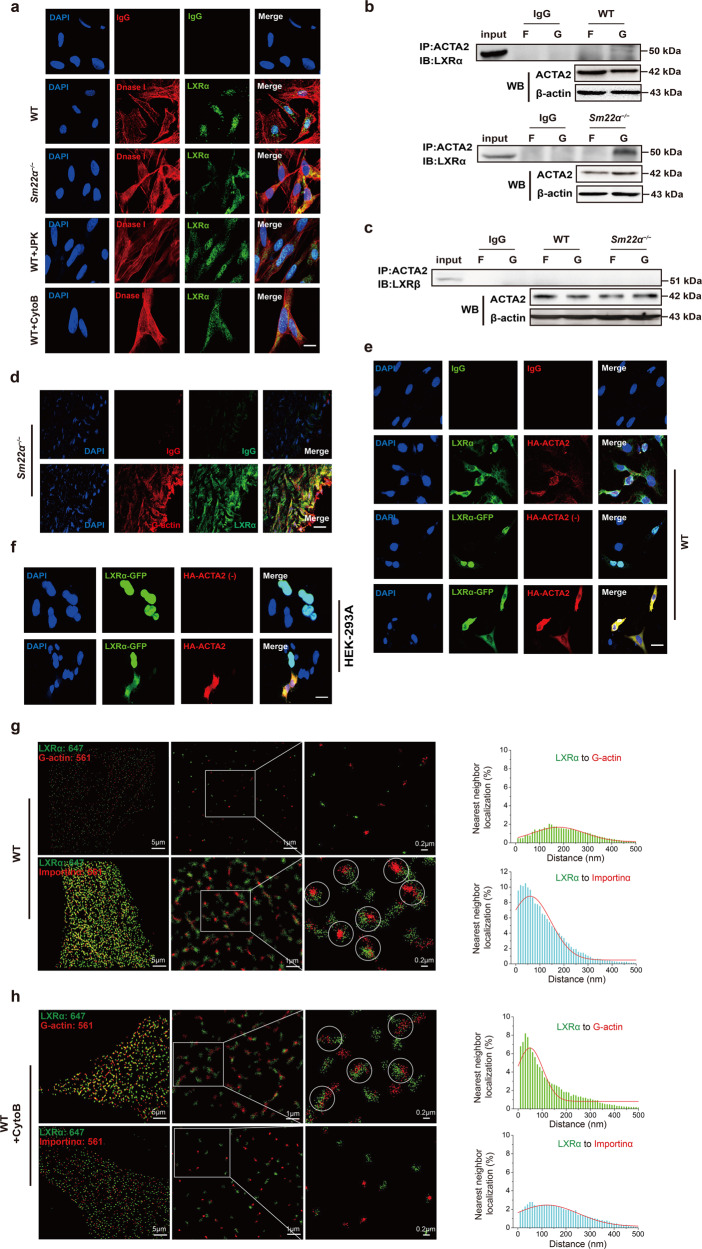
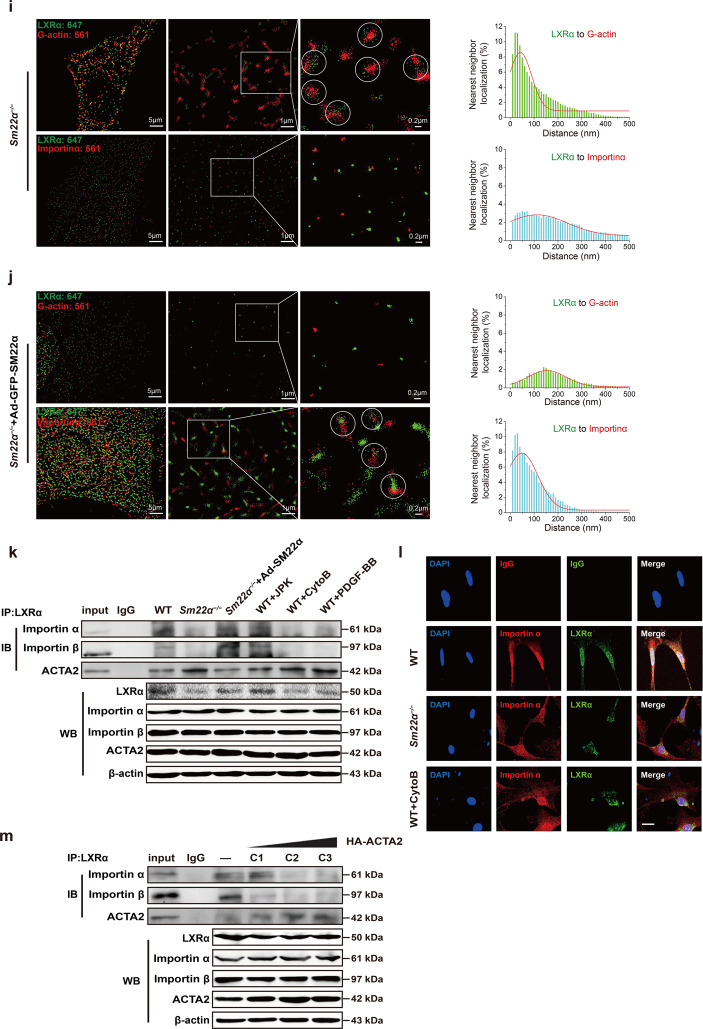
Fig. 5. G-actin interacts with and retains LXRα in the cytoplasm, blocking LXRα binding to Importin α.
a Double immunofluorescence staining for G-actin (DnaseI, red) and LXRα (green) in WT VSMCs accompanied with the treatment of JPK or CytoB and also in Sm22α−/− VSMCs. Scale bar, 10 μm. b, c Co-immunoprecipitation of ACTA2 and LXRα (b) and LXRβ (c) respectively in F- and G-actin fractions of WT and Sm22α−/− VSMCs (n = 3). d Double immunofluorescence staining of G-actin (Dnase1, red) and LXRα (green) or IgG in the atherosclerotic lesion in the aortic wall of Sm22α−/− mice. Scale bar, 20 μm. e Representative immunofluorescence staining for endogenous LXRα (green) and LXRα-GFP (green) in WT VSMCs transfected with HA-ACTA2 (red, stained by anti-HA antibody) or not. Scale bar, 15 μm. f Representative immunofluorescence staining for LXRα-GFP (green) and HA-ACTA2 (red, stained by anti-HA antibody) in HEK-293A cells. Scale bar, 10 μm. g−j Two-color STORM images and quantification of the colocalization degree between LXRα and G-actin as well as Importin α in WT VSMCs with (h) or without (g) CytoB treatment and Sm22α−/− VSMCs with (j) or without (i) Ad-GFP-SM22α infection (n > 10). k Co-immunoprecipitation of LXRα and Improtin α, Improtin β or ACTA2 in WT and Sm22α−/− VSMCs with or without JPK, CytoB, PDGF-BB and Ad-GFP-SM22α treatment (n = 3). l Double immunofluorescence staining for Importin α (red) and LXRα (green) in WT and Sm22α−/− VSMCs as well as CytoB-treated WT VSMCs. Scale bar, 15 μm. m Co-immunoprecipitation of LXRα and Importin α, Improtin β or ACTA2 in WT VSMCs transfected with HA-ACTA2 of different concentrations (n = 3). Data and images represent at least three independent experiments.