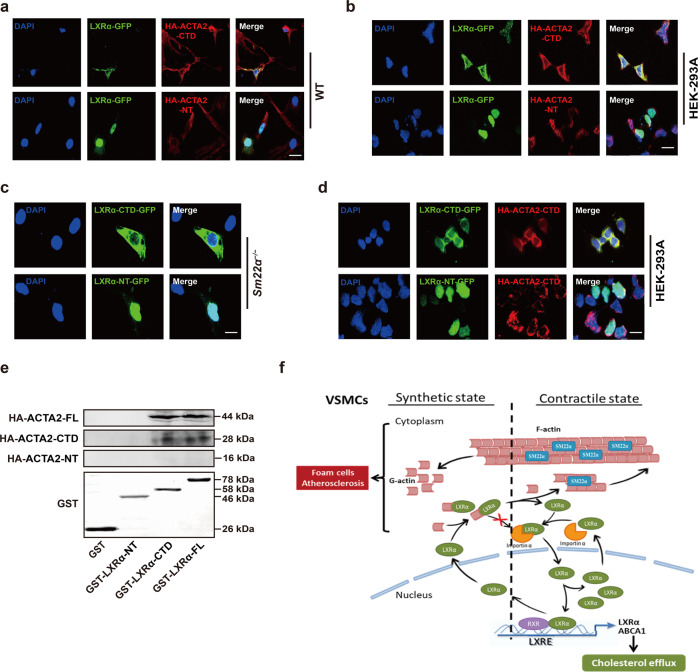
Fig. 6. The C-terminal domain mediates the interaction between G-actin and LXRα.
a Representative immunofluorescence staining for LXRα-GFP (green) in WT VSMCs transfected with HA-ACTA2-CTD (red) or HA-ACTA2-NT (red). Scale bar, 15 μm. b Representative immunofluorescence staining for LXRα-GFP (green) and HA-ACTA2-CTD (red) or HA-ACTA2-NT (red) in HEK-293A cells. Scale bar, 15 μm. c LXRα-CTD-GFP (green) or LXRα-NT-GFP (green) was transfected into Sm22α−/− VSMCs. Scale bar, 10 μm. d LXRα (-CTD, -NT)-GFP (green) and HA-ACTA2-CTD (red) were co-expressed in HEK-293A cells. Scale bar, 10 μm. e Interaction of HA-ACTA2 (-FL, -CTD, -NT) and GST-LXRα (-FL, -CTD, -NT) proteins analyzed by in vitro pull-down assay (n = 3). f Schematic representation of a working model in which SM22α inhibits VSMC-derived foam cell formation by blocking actin-LXRα signaling ameliorating atherosclerosis. Data and images represent at least three independent experiments.