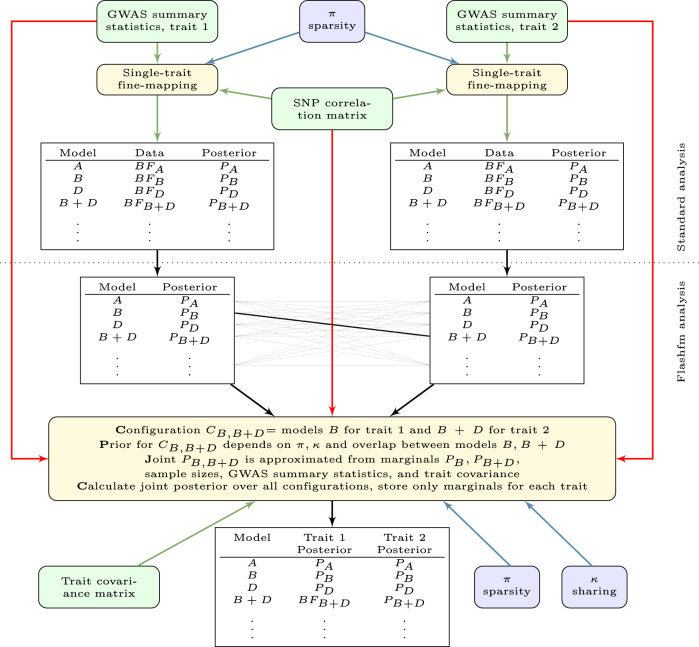
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram for flashfm.
Flashfm is used for multiple quantitative traits that are measured in the same studies, allowing for missing measurements and family data. First, standard analysis of single-trait fine-mapping is needed for each trait. Then the model posterior probabilities (PPs) from each of these marginal fine-mapping analyses are combined in flashfm, using an approximation to the joint PP, based on an approximation of the joint Bayes’ factor. In addition to a SNP correlation matrix, a trait covariance approximation is also needed. Information is shared between traits via a sharing prior that upweights joint models with shared causal variants by a factor of Ҝ. Memory requirements are reduced by storing only the trait-adjusted marginal PPs for each trait.