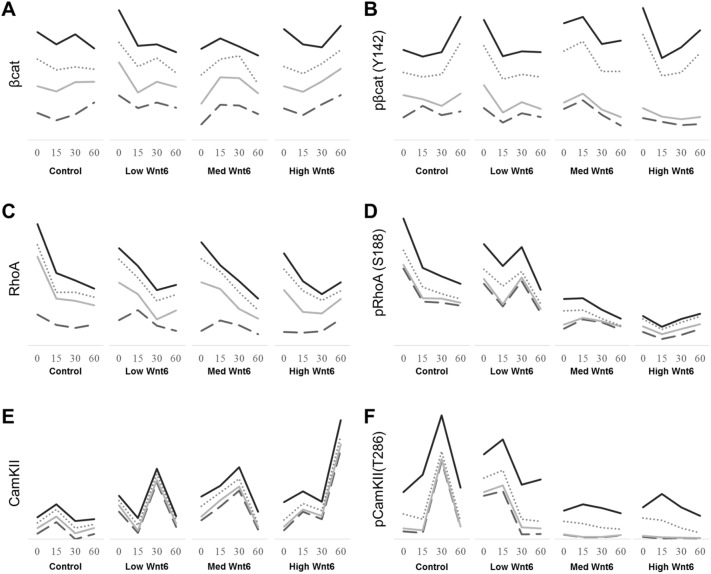
Figure 4.
Quantitation of proteins involved in the Wnt pathway upon exposure to Wnt6. Stacked trends of individual donors measuring (A) β-catenin, (B) phosphorylated β-catenin (Y142), (C) RhoA, (D) phosphorylated RhoA (S188), (E) CamKII, and (F) phosphorylated CamKII (T286) at 0, 15, 30, and 60 min after treatment with control, low-, medium-, and high-Wnt6 conditional medium (CM). Treatment with low-Wnt6 CM resulted in immediate increases in β-catenin concentration. Treatment with medium-Wnt6 CM resulted in increases 15 min after exposure. Treatment with high-Wnt6 CM increased β-catenin 60 min after exposure. Activation of β-catenin as determined by phosphorylated β-catenin (Y142) concentrations was observed immediately after treatment with low-, medium-, and high-Wnt6 CM. Control medium also activated β-catenin at 60 min from residual 3T3-expressed Wnt ligands. RhoA expression showed a general reduction, whereas phosphorylation of RhoA was lost immediately upon treatment with medium- or high-Wnt6 CM. An increase in CamKII expression was detected almost immediately after Wnt6 treatment, and maximum levels were detected 30–60 min after Wnt6 treatment. Phosphorylation of CamKII was lost immediately during medium- or high-Wnt6 CM treatment. Each line represents the quantities from individual donors. Donor 1, solid black, 9000 cells/cm2; Donor 2, dotted gray, 3250 cells/cm2; Donor 3, solid gray, 8000 cells/cm2; Donor 4, gray dash, 13,500 cells/cm2. Normalized to GAPDH. Phosphorylated proteins were normalized to the levels of their unphosphorylated counterparts.