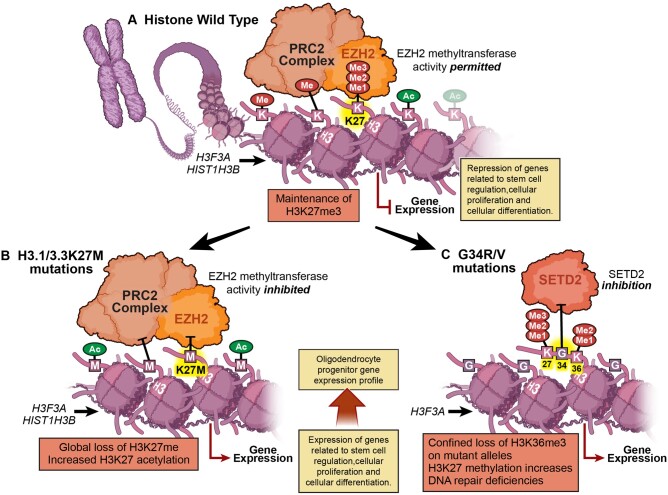
Figure 2.
Histone mutations in pHGGs. (A) In histone wild-type pHGGs, there is maintenance of global H3K27me3 across the genome. (B) However, in H3.1 or H3.3K27M mutant pHGGs, the methyltransferase activity of the EZH2 enzymatic unit of the PRC2 complex is inhibited, resulting in global hypomethylation and increased acetylation. (C) In H3.3G34R/V mutant pHGGs, there is loss of H3K27me3 but only on affected histone proteins, due to the proximity of the G34 position to K36.