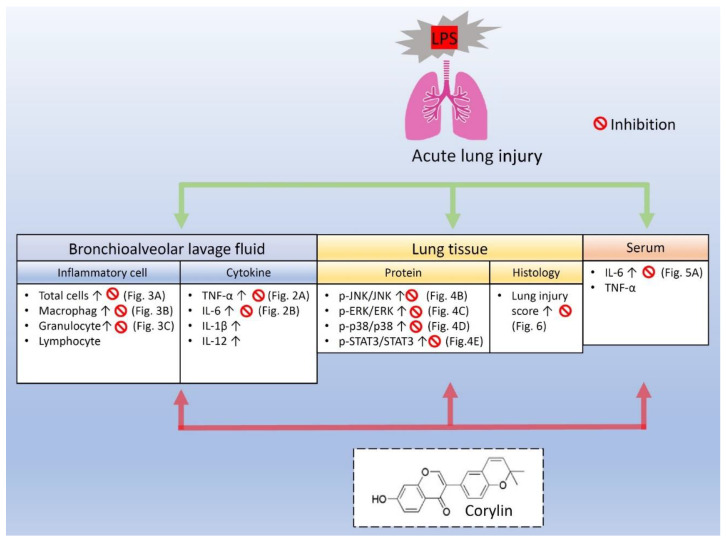
Figure 7.
Anti-inflammatory effect of corylin on LPS-induced ALI. The experimental results demonstrated that corylin attenuated the overproduction of IL-6 in LPS-activated human bronchial epithelial cells. In intratracheal LPS-induced ALI mice, corylin attenuated tissue damages, suppressed inflammatory cell infiltration, and decreased secretion of IL-6 and TNF-α in the BALF and serum; moreover, it further inhibited the expression of phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including the expression of p-JNK/JNK, p-ERK/ERK, p-p38/p38, and repressed the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in lung. Taken together, our results are the first to demonstrate the anti-inflammatory effects of corylin on LPS-induced ALI and suggest corylin has significant potential as a novel therapeutic agent for ALI.