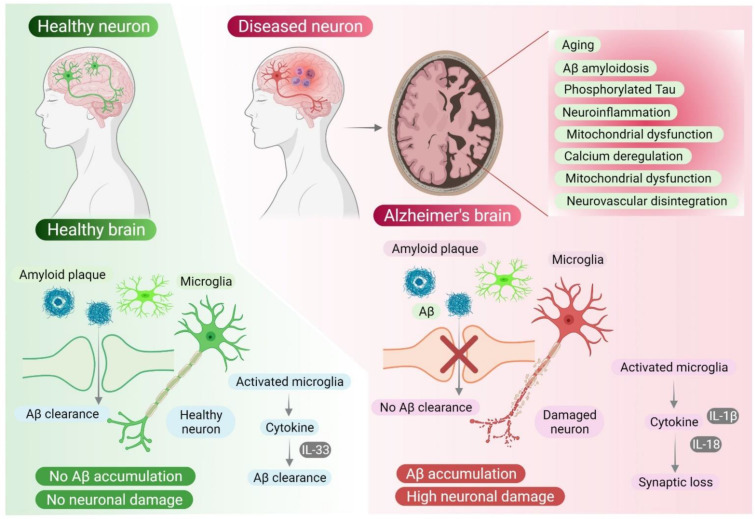
Figure 1.
The pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease is very complex. Major pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease are provided. Among all the hallmarks, Aβ accumulation is considered the major cause of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. It has been found that all other causes such as tau pathology and/or neuroinflammation ultimately converge to Aβ accumulation. For instance, microglia, the innate immune system of the nervous system, mediates neuroinflammation by the production of cytokines such as IL33, IL-8 and IL-1β. Microglial activation initiates inflammation of the neural tissues. The cytokines (IL-33) produced in the due process help in Aβ clearance whereas IL-8 and IL-1β cause synaptic dysfunction. This molecular mechanism reflects the complex.