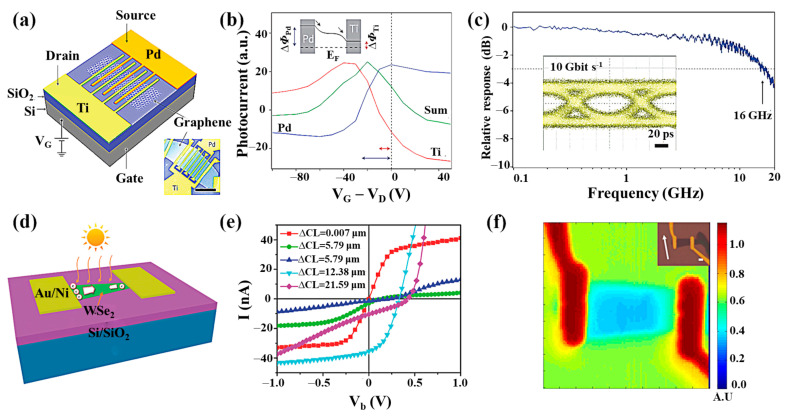
Figure 8.
Metal/2D material structures. (a) Metal–graphene–metal (MGM) photodetectors with asymmetric metal contacts. (b) The dotted line denotes the Fermi level. and represent the difference between the Dirac point energy and the Fermi level in palladium- and titanium-doped graphenes, respectively. (c) Relative photoresponse versus light intensity modulation frequency. The -3dB bandwidth of this MGM photodetector is 16 GHz. Inset: receiver eye-diagram obtained using this MGM photodetector, showing a completely open eye. (d) Photodetectors with asymmetric contact geometries. (e) Photodetectors with different degrees of asymmetries. (f) Weyl semimetal scanning photocurrent response. (a–c) reproduced with permission from [5]. Copyright Nature Publishing Group, 2010. (d,e) reproduced with permission from [90]. Copyright Wiley 2019. (f) Reproduced with permission from [91]. Copyright Nature Publishing Group, 2019.