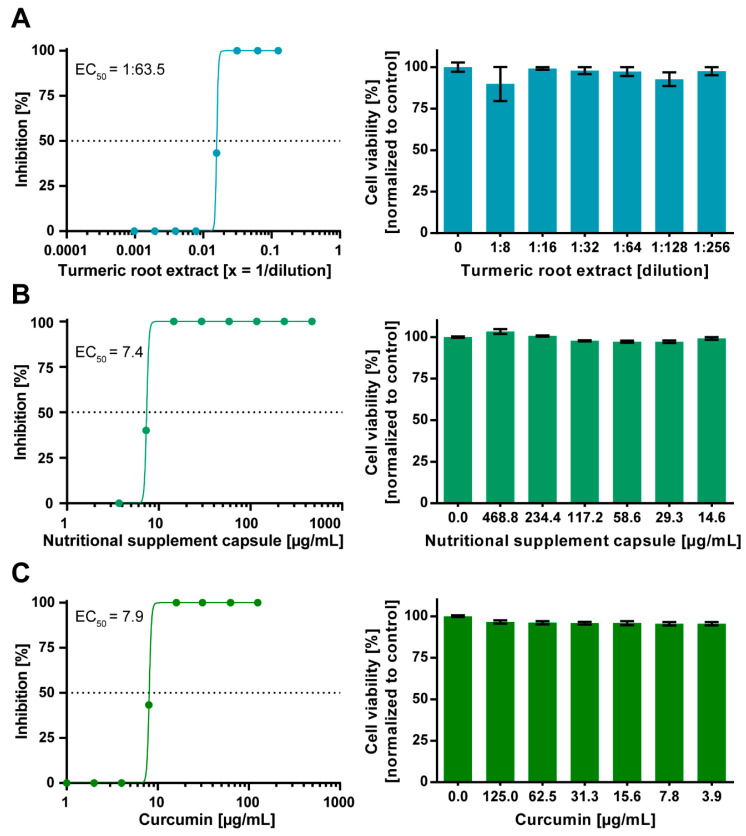
Figure 2.
Dose-dependent antiviral activity of aqueous turmeric root extract, curcumin-containing nutritional supplement capsules, and curcumin against SARS-CoV-2. Decreasing concentrations of aqueous turmeric root extract (1:8–1:1024 dilution) (A), nutritional supplement capsules (468.8–3.7 µg/mL) (B), and curcumin (125–1 µg/mL) (C) were pre-incubated with 100 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 for one hour. Subsequently, each dilution of virus–herb suspensions was incubated on confluent Vero E6 cells grown on a 96-well plate. After 48 h, cells were stained with crystal violet and analyzed regarding cytopathic effects. The half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) was calculated by nonlinear regression using GraphPad Prism. The cytotoxic effect of various concentrations of aqueous turmeric root extract, nutritional supplement capsules, and curcumin toward Vero E6 cells was determined by Orangu Cell Counting Solution (Cell guidance systems) after 48 h. Cell viability was normalized to untreated control cells. The experiment was performed three times independently. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).