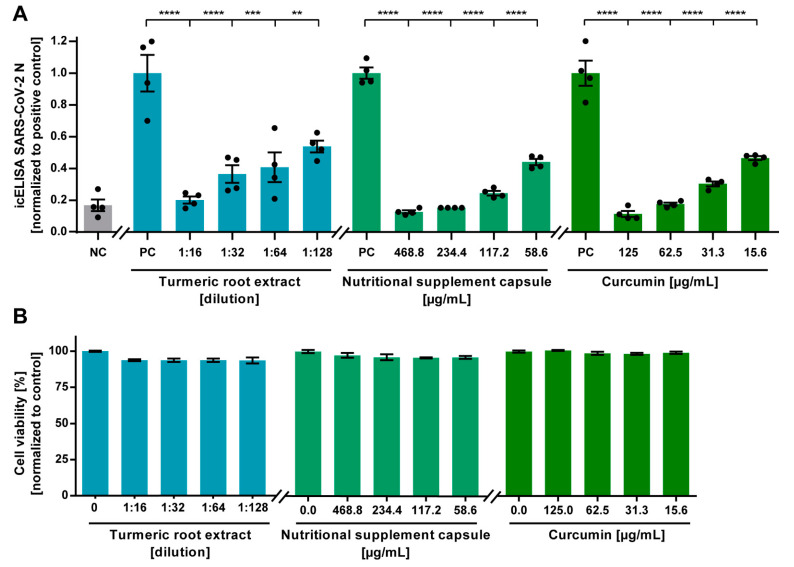
Figure 3.
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by aqueous turmeric root extract, curcumin-containing nutritional supplement capsules, and curcumin on a human cell line assessed by an in-cell ELISA (icELISA)-based neutralization test (icNT). (A) Decreasing concentrations of aqueous turmeric root extract (1:16–1:128 dilution), nutritional supplement capsule content (468.8–58.6 µg/mL), or curcumin (125–15.6 µg/mL) were pre-incubated with 5000 plaque-forming units (PFU) of SARS-CoV-2 for one hour. Subsequently, mixtures were added to human Calu-3 cells and incubated for 24 h. After incubation with a SARS-CoV-2 N-specific primary antibody and peroxidase-labelled secondary antibody, the enzyme reaction was visualized by adding tetramethylbenzidine. Absorbance was measured with a microplate multireader at OD450. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test using GraphPad Prism. ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; and **** p < 0.0001; error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). NC = negative control (medium); PC = positive control (5000 PFU SARS-CoV-2). (B) The cytotoxic effect of various concentrations of aqueous turmeric root extract, nutritional supplement capsule, and curcumin toward Calu-3 cells was determined by Orangu™ Cell Counting Solution (Cell guidance systems) after 24 h. The cell viability was normalized to untreated control cells. Error bars represent the SEM.