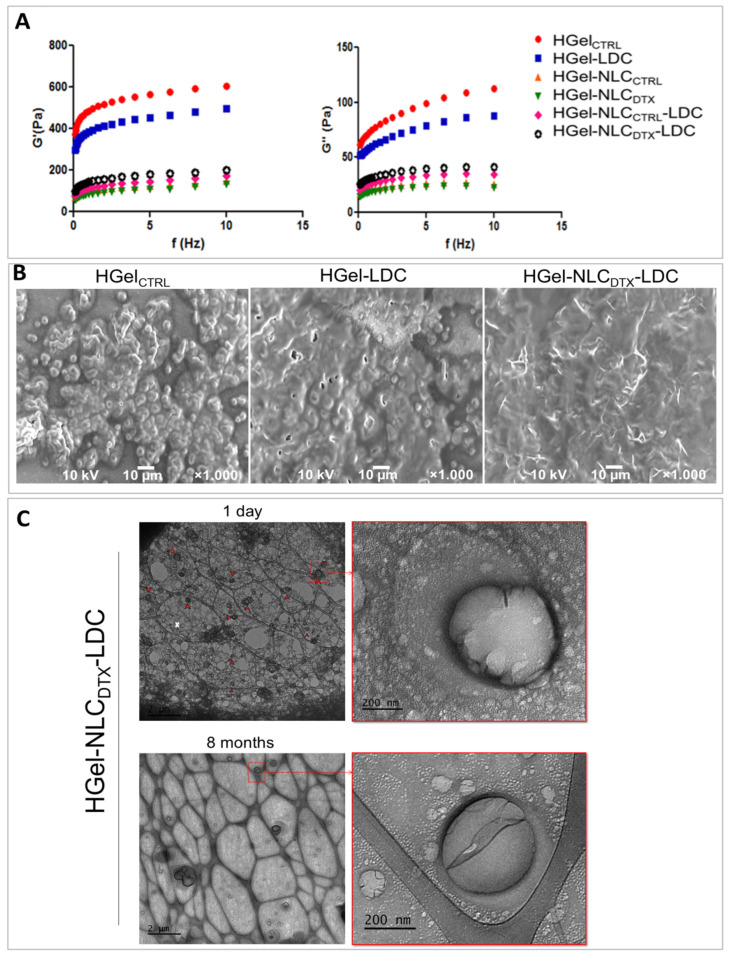
Figure 1.
(A) Determination of the viscoelastic properties of hydrogels using oscillatory rheometry, at 32.5 °C: Elasticity (G’)-left-and viscosity (G”) modulus-right; (B) FE-SEM micrographs of the hydrogels: control (HGelCTRL), with lidocaine (HGel-LDC) and with lidocaine plus NLCDTX (HGel-NLCDTX-LDC). Magnification: 1000×, 10 kV. (C) Cryo-EM of the hybrid hydrogel (HGel-NLCDTX-LDC), at 120 kV. Red arrows point to NLCDTX dispersed in the freshly prepared hydrogel (upper left). Notice that the spherical morphology of the NLC was preserved when adsorbed in the hydrogel lattice, even after 8 months (bottom). Magnification: 60,000× (left) and 120,000× (right).