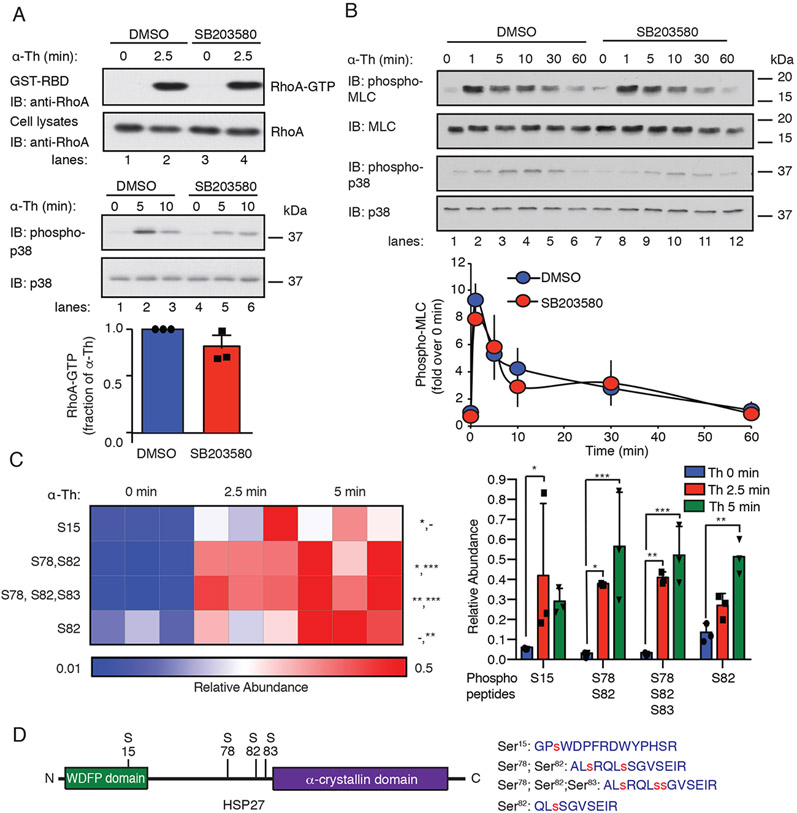
Fig. 1. Thrombin-induced p38 signaling is independent of the RhoA-MLC pathway and promotes HSP27 phosphorylation.
(A) Top: Assessment of RhoA activity in EA.hy926 cells pretreated with the 3 μM SB203580 (p38 inhibitor) or DMSO for 1 hour and stimulated with 10 nM thrombin (α-Th). Blots of RhoA and p38 are representative of three independent experiments. Bottom: Data in the bar graph are mean ± SD of three independent experiments and were analyzed by Student’s t test (not significant). (B) Top: Immunoblotting analysis of total and phosphorylated MLC and p38 in HUVECs pretreated with SB203580 or DMSO and the stimulated with α-Th for the indicated times. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. Bottom: Densitometric analysis of the fold-change in the relative abundances of the indicated phosphorylated proteins over time. Data are means ± SD of three independent experiments and were analyzed by Student’s t test (not significant). (C) Left: Heat map of HSP27 phospho-peptide site abundance induced by α-Th over time. Data were derived from three biological replicates. Increases and decreases in phospho-peptide abundance are indicated by the red and blue color intensities, respectively. Color intensities depict phospho-peptide abundances in each row induced by α-Th relative to the respective zero-time control. Right: Changes in HSP27 phospho-peptide abundance at the indicated times. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; -, not significant. (D) Left: Schematic of HSP27 containing an N-terminal WDFP motif and a C-terminal α-crystallin domain. Right: HSP27 phospho-peptides identified by MS analysis, where phosphorylated serine residues are indicated by the red “s”.