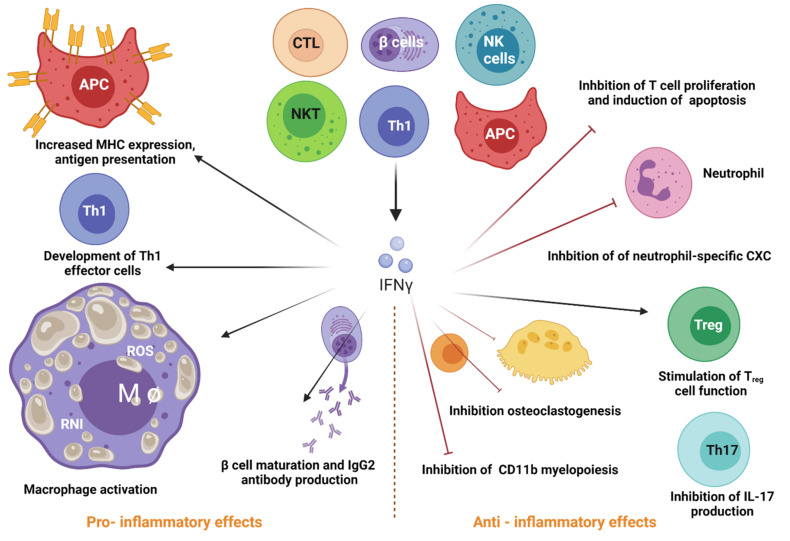
Figure 2.
Roles of Type II Interferons. IFN type II is a pleiotropic cytokine that participates in viral response and regulating innate and adaptive immune responses. NK cells, T cells, B cells, APC release this cytokine to function both as an inducer (pro-inflammatory) and a regulator (anti-inflammatory) of immune responses. Regarding the pro-inflammatory effects, IFN-γ has a strong macrophage-activating activity and induces B cell maturation and IgG2 production. Additionally, this cytokine stimulates antigen presentation via MHC, development of Th1 effector cells, and cell function of Treg cells. The anti-inflammatory effects of IFN-γ include the inhibition of T cell-dependent osteoclastogenesis and production of IL-17, which leads to decreased levels of neutrophil-specific CXC chemokines and limited mobilization of neutrophils. Furthermore, type II IFN inhibits myelopoiesis of CD11b+ leukocytes, T cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by secreting nitric oxide (NO) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). All these anti-inflammatory properties contribute to the protective role of IFN-γ against autoimmune diseases. Created with BioRender.com.